 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.6.1 under development (2024-12-17)
|
 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.6.1 under development (2024-12-17)
|
#include <visp3/vision/vpHomography.h>
 Inheritance diagram for vpHomography:
Inheritance diagram for vpHomography:Public Member Functions | |
| vpHomography () | |
| vpHomography (const vpHomography &H) | |
| vpHomography (const vpHomogeneousMatrix &aMb, const vpPlane &bP) | |
| vpHomography (const vpRotationMatrix &aRb, const vpTranslationVector &atb, const vpPlane &bP) | |
| vpHomography (const vpThetaUVector &tu, const vpTranslationVector &atb, const vpPlane &bP) | |
| vpHomography (const vpPoseVector &arb, const vpPlane &bP) | |
| vpHomography & | buildFrom (const vpRotationMatrix &aRb, const vpTranslationVector &atb, const vpPlane &bP) |
| vpHomography & | buildFrom (const vpThetaUVector &tu, const vpTranslationVector &atb, const vpPlane &bP) |
| vpHomography & | buildFrom (const vpPoseVector &arb, const vpPlane &bP) |
| vpHomography & | buildFrom (const vpHomogeneousMatrix &aMb, const vpPlane &bP) |
| vpHomography | collineation2homography (const vpCameraParameters &cam) const |
| vpMatrix | convert () const |
| void | computeDisplacement (vpRotationMatrix &aRb, vpTranslationVector &atb, vpColVector &n) |
| void | computeDisplacement (const vpColVector &nd, vpRotationMatrix &aRb, vpTranslationVector &atb, vpColVector &n) |
| double | det () const |
| void | eye () |
| vpHomography | homography2collineation (const vpCameraParameters &cam) const |
| vpHomography | inverse (double sv_threshold=1e-16, unsigned int *rank=nullptr) const |
| void | inverse (vpHomography &bHa) const |
| void | load (std::ifstream &f) |
| vpHomography | operator* (const vpHomography &H) const |
| vpHomography | operator* (const double &v) const |
| vpColVector | operator* (const vpColVector &b) const |
| vpPoint | operator* (const vpPoint &b_P) const |
| vpHomography | operator/ (const double &v) const |
| vpHomography & | operator/= (double v) |
| vpHomography & | operator= (const vpHomography &H) |
| vpHomography & | operator= (const vpMatrix &H) |
| vpImagePoint | projection (const vpImagePoint &ipb) |
| void | resize (unsigned int nrows, unsigned int ncols, bool flagNullify=true) |
| void | save (std::ofstream &f) const |
Inherited functionalities from vpArray2D | |
| unsigned int | getCols () const |
| double | getMaxValue () const |
| double | getMinValue () const |
| unsigned int | getRows () const |
| unsigned int | size () const |
| void | resize (unsigned int nrows, unsigned int ncols, bool flagNullify=true, bool recopy_=true) |
| void | reshape (unsigned int nrows, unsigned int ncols) |
| void | insert (const vpArray2D< double > &A, unsigned int r, unsigned int c) |
| bool | operator== (const vpArray2D< double > &A) const |
| bool | operator!= (const vpArray2D< double > &A) const |
| double * | operator[] (unsigned int i) |
| double * | operator[] (unsigned int i) const |
| vpArray2D< double > | hadamard (const vpArray2D< double > &m) const |
| vpArray2D< double > | t () const |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static void | DLT (const std::vector< double > &xb, const std::vector< double > &yb, const std::vector< double > &xa, const std::vector< double > &ya, vpHomography &aHb, bool normalization=true) |
| static void | HLM (const std::vector< double > &xb, const std::vector< double > &yb, const std::vector< double > &xa, const std::vector< double > &ya, bool isplanar, vpHomography &aHb) |
| static bool | ransac (const std::vector< double > &xb, const std::vector< double > &yb, const std::vector< double > &xa, const std::vector< double > &ya, vpHomography &aHb, std::vector< bool > &inliers, double &residual, unsigned int nbInliersConsensus, double threshold, bool normalization=true) |
| static vpImagePoint | project (const vpCameraParameters &cam, const vpHomography &bHa, const vpImagePoint &iPa) |
| static vpPoint | project (const vpHomography &bHa, const vpPoint &Pa) |
| static void | robust (const std::vector< double > &xb, const std::vector< double > &yb, const std::vector< double > &xa, const std::vector< double > &ya, vpHomography &aHb, std::vector< bool > &inliers, double &residual, double weights_threshold=0.4, unsigned int niter=4, bool normalization=true) |
Public Attributes | |
| double * | data |
Related Functions | |
(Note that these are not member functions.) | |
| enum | vpGEMMmethod |
| bool | operator== (const vpArray2D< double > &A) const |
| bool | operator== (const vpArray2D< float > &A) const |
| bool | operator!= (const vpArray2D< double > &A) const |
| void | vpGEMM (const vpArray2D< double > &A, const vpArray2D< double > &B, const double &alpha, const vpArray2D< double > &C, const double &beta, vpArray2D< double > &D, const unsigned int &ops=0) |
Inherited I/O from vpArray2D with Static Public Member Functions | |
| vpArray2D< double > | insert (const vpArray2D< double > &A, const vpArray2D< double > &B, unsigned int r, unsigned int c) |
| static bool | load (const std::string &filename, vpArray2D< double > &A, bool binary=false, char *header=nullptr) |
| static bool | loadYAML (const std::string &filename, vpArray2D< double > &A, char *header=nullptr) |
| static bool | save (const std::string &filename, const vpArray2D< double > &A, bool binary=false, const char *header="") |
| static bool | saveYAML (const std::string &filename, const vpArray2D< double > &A, const char *header="") |
| static vpArray2D< double > | conv2 (const vpArray2D< double > &M, const vpArray2D< double > &kernel, const std::string &mode) |
| static void | conv2 (const vpArray2D< double > &M, const vpArray2D< double > &kernel, vpArray2D< double > &res, const std::string &mode) |
| static void | insert (const vpArray2D< double > &A, const vpArray2D< double > &B, vpArray2D< double > &C, unsigned int r, unsigned int c) |
| unsigned int | rowNum |
| unsigned int | colNum |
| double ** | rowPtrs |
| unsigned int | dsize |
Implementation of an homography and operations on homographies.
This class aims to compute the homography wrt. two images [34].
The vpHomography class is derived from vpArray2D<double>.
These two images are both described by a set of points. The 2 sets (one per image) are sets of corresponding points : for a point in a image, there is the corresponding point (image of the same 3D point) in the other image points set. These 2 sets are the only data needed to compute the homography. One method used is the one introduced by Ezio Malis during his PhD [28]. A normalization is carried out on this points in order to improve the conditioning of the problem, what leads to improve the stability of the result.
Store and compute the homography such that
![]()
with
![]()
The Tutorial: Homography estimation from points explains how to use this class.
The example below shows also how to manipulate this class to first compute a ground truth homography from camera poses, project pixel coordinates points using an homography and lastly estimate an homography from a subset of 4 matched points in frame a and frame b respectively.
Definition at line 173 of file vpHomography.h.
| BEGIN_VISP_NAMESPACE vpHomography::vpHomography | ( | ) |
Initialize an homography as identity.
Definition at line 53 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References eye().
| vpHomography::vpHomography | ( | const vpHomography & | H | ) |
Initialize an homography from another homography.
Definition at line 55 of file vpHomography.cpp.
| vpHomography::vpHomography | ( | const vpHomogeneousMatrix & | aMb, |
| const vpPlane & | bP | ||
| ) |
Construction from translation and rotation and a plane.
Definition at line 57 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References buildFrom().
| vpHomography::vpHomography | ( | const vpRotationMatrix & | aRb, |
| const vpTranslationVector & | atb, | ||
| const vpPlane & | bP | ||
| ) |
Construction from translation and rotation and a plane.
Definition at line 68 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References buildFrom().
| vpHomography::vpHomography | ( | const vpThetaUVector & | tu, |
| const vpTranslationVector & | atb, | ||
| const vpPlane & | bP | ||
| ) |
Construction from translation and rotation and a plane.
Definition at line 62 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References buildFrom().
| vpHomography::vpHomography | ( | const vpPoseVector & | arb, |
| const vpPlane & | bP | ||
| ) |
Construction from translation and rotation and a plane.
Definition at line 74 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References buildFrom().
| vpHomography & vpHomography::buildFrom | ( | const vpHomogeneousMatrix & | aMb, |
| const vpPlane & | bP | ||
| ) |
Construction from homogeneous matrix and a plane.
Definition at line 79 of file vpHomography.cpp.
| vpHomography & vpHomography::buildFrom | ( | const vpPoseVector & | arb, |
| const vpPlane & | bP | ||
| ) |
Construction from translation and rotation and a plane.
Definition at line 105 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpHomogeneousMatrix::buildFrom().
| vpHomography & vpHomography::buildFrom | ( | const vpRotationMatrix & | aRb, |
| const vpTranslationVector & | atb, | ||
| const vpPlane & | bP | ||
| ) |
Construction from translation and rotation and a plane.
Definition at line 96 of file vpHomography.cpp.
Referenced by vpHomography().
| vpHomography & vpHomography::buildFrom | ( | const vpThetaUVector & | tu, |
| const vpTranslationVector & | atb, | ||
| const vpPlane & | bP | ||
| ) |
Construction from translation and rotation and a plane.
Definition at line 87 of file vpHomography.cpp.
| vpHomography vpHomography::collineation2homography | ( | const vpCameraParameters & | cam | ) | const |
Transform an homography from pixel space to calibrated domain.
Given homography ![]() corresponding to the collineation matrix in the pixel space, compute the homography matrix
corresponding to the collineation matrix in the pixel space, compute the homography matrix ![]() in the Euclidean space or calibrated domain using:
in the Euclidean space or calibrated domain using:
![]()
| [in] | cam | : Camera parameters used to fill
|
Definition at line 609 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpCameraParameters::get_px(), vpCameraParameters::get_px_inverse(), vpCameraParameters::get_py(), vpCameraParameters::get_py_inverse(), vpCameraParameters::get_u0(), and vpCameraParameters::get_v0().
| void vpHomography::computeDisplacement | ( | const vpColVector & | nd, |
| vpRotationMatrix & | aRb, | ||
| vpTranslationVector & | atb, | ||
| vpColVector & | n | ||
| ) |
Compute the camera displacement between two images from the homography ![]() which is here an implicit parameter (*this).
which is here an implicit parameter (*this).
Camera displacement between ![]() and
and ![]() is represented as a rotation matrix
is represented as a rotation matrix ![]() and a translation vector
and a translation vector 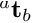 from which an homogeneous matrix can be build (vpHomogeneousMatrix).
from which an homogeneous matrix can be build (vpHomogeneousMatrix).
| nd | : Input normal vector to the plane used to compar with the normal vector n extracted from the homography. |
| aRb | : Rotation matrix as an output |
| atb | : Translation vector as an output 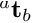 . . |
| n | : Normal vector to the plane as an output. |
Definition at line 58 of file vpHomographyExtract.cpp.
References computeDisplacement().
| void vpHomography::computeDisplacement | ( | vpRotationMatrix & | aRb, |
| vpTranslationVector & | atb, | ||
| vpColVector & | n | ||
| ) |
Compute the camera displacement between two images from the homography ![]() which is here an implicit parameter (*this).
which is here an implicit parameter (*this).
| aRb | : Rotation matrix as an output |
| atb | : Translation vector as an output 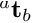 . . |
| n | : Normal vector to the plane as an output. |
Definition at line 47 of file vpHomographyExtract.cpp.
Referenced by computeDisplacement().
|
staticinherited |
Perform a 2D convolution similar to Matlab conv2 function: ![]() .
.
| M | : First matrix. |
| kernel | : Second matrix. |
| mode | : Convolution mode: "full" (default), "same", "valid". |
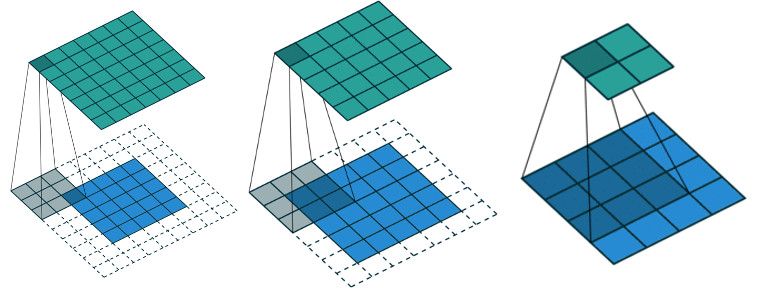
Definition at line 1053 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
staticinherited |
Perform a 2D convolution similar to Matlab conv2 function: ![]() .
.
| M | : First array. |
| kernel | : Second array. |
| res | : Result. |
| mode | : Convolution mode: "full" (default), "same", "valid". |

Definition at line 1067 of file vpArray2D.h.
| vpMatrix vpHomography::convert | ( | ) | const |
Converts an homography to a matrix.
Definition at line 596 of file vpHomography.cpp.
| double vpHomography::det | ( | ) | const |
Return homography determinant.
Definition at line 382 of file vpHomography.cpp.
|
static |
From couples of matched points ![]() in image a and
in image a and ![]() in image b with homogeneous coordinates, computes the homography matrix by resolving
in image b with homogeneous coordinates, computes the homography matrix by resolving ![]() using the DLT (Direct Linear Transform) algorithm.
using the DLT (Direct Linear Transform) algorithm.
At least 4 couples of points are needed.
To do so, we use the DLT algorithm on the data, ie we resolve the linear system by SDV : ![]() where
where ![]() is the vector with the terms of
is the vector with the terms of ![]() and
and ![]() depends on the points coordinates.
depends on the points coordinates.
For each point, in homogeneous coordinates we have:
![]()
which is equivalent to:
![]()
If we note ![]() the
the ![]() line of
line of ![]() , we can write:
, we can write:
![]()
Setting ![]() , the cross product can be rewritten by:
, the cross product can be rewritten by:
![]()
![\[ \underbrace{\left( \begin{array}{ccc}\mathbf{0}^T & -w_{a} \; ^b{\bf p}^T & y_{a} \; ^b{\bf p}^T \\ w_{a} \; ^b{\bf p}^T&\mathbf{0}^T & -x_{a} \; ^b{\bf p}^T \\ -y_{a} \; ^b{\bf p}^T & x_{a} \; ^b{\bf p}^T & \mathbf{0}^T\end{array}\right)}_{\mathbf{A}_i (3\times 9)} \underbrace{\left( \begin{array}{c}\mathbf{h}_{1}^{T} \\ \mathbf{h}_{2}^{T}\\\mathbf{h}_{3}^{T}\end{array}\right)}_{\mathbf{h} (9\times 1)}=0 \]](form_982.png)
leading to an homogeneous system to be solved: ![]() with
with ![]() .
.
It can be solved using an SVD decomposition:
![]()
h is the column of V associated with the smallest singular value of A
| xb,yb | : Coordinates vector of matched points in image b. These coordinates are expressed in meters. |
| xa,ya | : Coordinates vector of matched points in image a. These coordinates are expressed in meters. |
| aHb | : Estimated homography that relies the transformation from image a to image b. |
| normalization | : When set to true, the coordinates of the points are normalized. The normalization carried out is the one preconized by Hartley. |
| vpMatrixException::rankDeficient | : When the rank of the matrix that should be 8 is deficient. |
Definition at line 195 of file vpHomographyDLT.cpp.
References vpException::dimensionError, vpException::fatalError, vpMatrix::getCol(), vpMatrixException::rankDeficient, vpArray2D< Type >::resize(), and vpMatrix::svd().
Referenced by ransac().
| void vpHomography::eye | ( | ) |
Set the homography as identity transformation by setting the diagonal to 1 and all other values to 0.
Definition at line 389 of file vpHomography.cpp.
Referenced by vpHomography().
|
inlineinherited |
Return the number of columns of the 2D array.
Definition at line 337 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
inherited |
Return the array max value.
Definition at line 339 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
inherited |
Return the array min value.
Definition at line 341 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
inlineinherited |
Return the number of rows of the 2D array.
Definition at line 347 of file vpArray2D.h.
Compute the Hadamard product (element wise matrix multiplication).
| m | : Second matrix; |
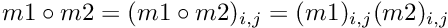
Definition at line 641 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
static |
From couples of matched points ![]() in image a and
in image a and ![]() in image b with homogeneous coordinates, computes the homography matrix by resolving
in image b with homogeneous coordinates, computes the homography matrix by resolving ![]() using Ezio Malis linear method (HLM) [27].
using Ezio Malis linear method (HLM) [27].
This method can consider points that are planar or non planar. The algorithm for planar scene implemented in this file is described in Ezio Malis PhD thesis [28].
| xb,yb | : Coordinates vector of matched points in image b. These coordinates are expressed in meters. |
| xa,ya | : Coordinates vector of matched points in image a. These coordinates are expressed in meters. |
| isplanar | : If true the points are assumed to be in a plane, otherwise there are assumed to be non planar. |
| aHb | : Estimated homography that relies the transformation from image a to image b. |
If the boolean isplanar is true the points are assumed to be in a plane otherwise there are assumed to be non planar.
Definition at line 605 of file vpHomographyMalis.cpp.
References vpException::dimensionError, and vpException::fatalError.
Referenced by vpPose::poseFromRectangle().
| vpHomography vpHomography::homography2collineation | ( | const vpCameraParameters & | cam | ) | const |
Transform an homography from calibrated domain to pixel space.
Given homography ![]() in the Euclidean space or in the calibrated domain, compute the homography
in the Euclidean space or in the calibrated domain, compute the homography ![]() corresponding to the collineation matrix in the pixel space using:
corresponding to the collineation matrix in the pixel space using:
![]()
| [in] | cam | : Camera parameters used to fill
|
Definition at line 647 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpCameraParameters::get_px(), vpCameraParameters::get_px_inverse(), vpCameraParameters::get_py(), vpCameraParameters::get_py_inverse(), vpCameraParameters::get_u0(), and vpCameraParameters::get_v0().
Referenced by project().
|
inherited |
Insert array B in array A at the given position.
| A | : Main array. |
| B | : Array to insert. |
| r | : Index of the row where to add the array. |
| c | : Index of the column where to add the array. |
Definition at line 1081 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
inlineinherited |
Insert array A at the given position in the current array.
| A | : The array to insert. |
| r | : The index of the row to begin to insert data. |
| c | : The index of the column to begin to insert data. |
Definition at line 497 of file vpArray2D.h.
| vpHomography vpHomography::inverse | ( | double | sv_threshold = 1e-16, |
| unsigned int * | rank = nullptr |
||
| ) | const |
Return inverted homography.
| [in] | sv_threshold | : Threshold used to test the singular values. If a singular value is lower than this threshold we consider that the homography is not full rank. |
| [out] | rank | : Rank of the homography that should be 3. |
Definition at line 130 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpArray2D< Type >::getCols(), vpArray2D< Type >::getRows(), and vpMatrix::pseudoInverse().
Referenced by inverse().
| void vpHomography::inverse | ( | vpHomography & | bHa | ) | const |
Invert the homography.
| bHa | : |
Definition at line 150 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References inverse().
|
inlinestaticinherited |
Load a matrix from a file.
| filename | : Absolute file name. |
| A | : Array to be loaded |
| binary | : If true the matrix is loaded from a binary file, else from a text file. |
| header | : Header of the file is loaded in this parameter. |
Definition at line 669 of file vpArray2D.h.
| void vpHomography::load | ( | std::ifstream & | f | ) |
Read an homography in a file, verify if it is really an homogeneous matrix.
| f | : the file. This file has to be written using save(). |
Definition at line 293 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpException::ioError.
|
inlinestaticinherited |
Load an array from a YAML-formatted file.
| filename | : absolute file name. |
| A | : array to be loaded from the file. |
| header | : header of the file is loaded in this parameter. |
Definition at line 783 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
inherited |
Not equal to comparison operator of a 2D array.
Definition at line 523 of file vpArray2D.h.
| vpHomography vpHomography::operator* | ( | const double & | v | ) | const |
Multiply an homography by a scalar.
| v | : Value of the scalar. |
Definition at line 197 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpArray2D< double >::data, and vpArray2D< Type >::data.
| vpColVector vpHomography::operator* | ( | const vpColVector & | b | ) | const |
Operation a = aHb * b.
| b | : 3 dimension vector. |
Definition at line 178 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpException::dimensionError, and vpArray2D< Type >::size().
| vpHomography vpHomography::operator* | ( | const vpHomography & | H | ) | const |
Multiplication by an homography.
| H | : Homography to multiply with. |
Definition at line 162 of file vpHomography.cpp.
From the coordinates of the point in image plane b and the homography between image a and b computes the coordinates of the point in image plane a.
| b_P | : 2D coordinates of the point in the image plane b. |
Definition at line 209 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpPoint::get_w(), vpPoint::get_x(), vpPoint::get_y(), vpPoint::set_w(), vpPoint::set_x(), and vpPoint::set_y().
| vpHomography vpHomography::operator/ | ( | const double & | v | ) | const |
Divide an homography by a scalar.
| v | : Value of the scalar. |
Definition at line 230 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpArray2D< double >::data, vpArray2D< Type >::data, and vpException::divideByZeroError.
| vpHomography & vpHomography::operator/= | ( | double | v | ) |
Divide all the element of the homography matrix by v : Hij = Hij / v
Definition at line 247 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpArray2D< double >::data, and vpException::divideByZeroError.
| vpHomography & vpHomography::operator= | ( | const vpHomography & | H | ) |
Copy operator. Allow operation such as aHb = H
| H | : Homography matrix to be copied. |
Definition at line 263 of file vpHomography.cpp.
| vpHomography & vpHomography::operator= | ( | const vpMatrix & | H | ) |
Copy operator. Allow operation such as aHb = H
| H | : Matrix to be copied. |
Definition at line 277 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpException::dimensionError, vpArray2D< Type >::getCols(), and vpArray2D< Type >::getRows().
Equal to comparison operator of a 2D array.
Definition at line 519 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
inlineinherited |
Set element 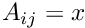 using A[i][j] = x.
using A[i][j] = x.
Definition at line 605 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
inlineinherited |
Get element 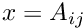 using x = A[i][j].
using x = A[i][j].
Definition at line 607 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
static |
Given iPa a pixel with coordinates ![]() in image a, and the homography
in image a, and the homography bHa in the Euclidean space or calibrated domain that links image a and b, computes the coordinates of the pixel ![]() in the image b using the camera parameters matrix
in the image b using the camera parameters matrix ![]() .
.
Compute ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]()
Definition at line 404 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpImagePoint::get_u(), vpImagePoint::get_v(), and homography2collineation().
|
static |
Given Pa a point with normalized coordinates ![]() in the image plane a, and the homography
in the image plane a, and the homography bHa in the Euclidean space that links image a and b, computes the normalized coordinates of the point ![]() in the image plane b.
in the image plane b.
Compute ![]() with
with ![]() and
and ![]()
Definition at line 418 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpPoint::get_x(), vpPoint::get_y(), vpPoint::set_x(), and vpPoint::set_y().
| vpImagePoint vpHomography::projection | ( | const vpImagePoint & | ipb | ) |
Project the current image point (in frame b) into the frame a using the homography aHb.
| ipb | : Homography defining the relation between frame a and frame b. |
Definition at line 578 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpImagePoint::get_u(), vpImagePoint::get_v(), vpImagePoint::set_u(), and vpImagePoint::set_v().
|
static |
From couples of matched points ![]() in image a and
in image a and ![]() in image b with homogeneous coordinates, computes the homography matrix by resolving
in image b with homogeneous coordinates, computes the homography matrix by resolving ![]() using Ransac algorithm.
using Ransac algorithm.
| xb,yb | : Coordinates vector of matched points in image b. These coordinates are expressed in meters. |
| xa,ya | : Coordinates vector of matched points in image a. These coordinates are expressed in meters. |
| aHb | : Estimated homography that relies the transformation from image a to image b. |
| inliers | : Vector that indicates if a matched point is an inlier (true) or an outlier (false). |
| residual | : Global residual computed as 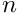 the number of inliers. the number of inliers. |
| nbInliersConsensus | : Minimal number of points requested to fit the estimated homography. |
| threshold | : Threshold for outlier removing. A point is considered as an outlier if the reprojection error |
| normalization | : When set to true, the coordinates of the points are normalized. The normalization carried out is the one preconized by Hartley. |
Definition at line 347 of file vpHomographyRansac.cpp.
References vpException::dimensionError, DLT(), and vpException::fatalError.
|
inlineinherited |
Definition at line 456 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
inline |
This function is not applicable to an homography that is always a 3-by-3 matrix.
| vpException::fatalError | When this function is called. |
Definition at line 409 of file vpHomography.h.
References vpException::fatalError.
Referenced by robust().
|
inlineinherited |
Set the size of the array and initialize all the values to zero.
| nrows | : number of rows. |
| ncols | : number of column. |
| flagNullify | : if true, then the array is re-initialized to 0 after resize. If false, the initial values from the common part of the array (common part between old and new version of the array) are kept. Default value is true. |
| recopy_ | : if true, will perform an explicit recopy of the old data. |
Definition at line 362 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
static |
From couples of matched points ![]() in image a and
in image a and ![]() in image b with homogeneous coordinates, computes the homography matrix by resolving
in image b with homogeneous coordinates, computes the homography matrix by resolving ![]() using a robust estimation scheme.
using a robust estimation scheme.
This method is to compare to DLT() except that here a robust estimator is used to reject couples of points that are considered as outliers.
At least 4 couples of points are needed.
| xb,yb | : Coordinates vector of matched points in image b. These coordinates are expressed in meters. |
| xa,ya | : Coordinates vector of matched points in image a. These coordinates are expressed in meters. |
| aHb | : Estimated homography that relies the transformation from image a to image b. |
| inliers | : Vector that indicates if a matched point is an inlier (true) or an outlier (false). |
| residual | : Global residual computed as 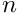 the number of inliers. the number of inliers. |
| weights_threshold | : Threshold applied on the weights updated during the robust estimation and used to consider if a point is an outlier or an inlier. Values should be in [0:1]. A couple of matched points that have a weight lower than this threshold is considered as an outlier. A value equal to zero indicates that all the points are inliers. |
| niter | : Number of iterations of the estimation process. |
| normalization | : When set to true, the coordinates of the points are normalized. The normalization carried out is the one preconized by Hartley. |
Definition at line 434 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpArray2D< Type >::data, vpException::dimensionError, vpException::fatalError, vpRobust::MEstimator(), vpMatrix::pseudoInverse(), resize(), and vpRobust::TUKEY.
|
inlinestaticinherited |
Save a matrix to a file.
| filename | : Absolute file name. |
| A | : Array to be saved. |
| binary | : If true the matrix is saved in a binary file, else a text file. |
| header | : Optional line that will be saved at the beginning of the file. |
Warning : If you save the matrix as in a text file the precision is less than if you save it in a binary file.
Definition at line 874 of file vpArray2D.h.
| void vpHomography::save | ( | std::ofstream & | f | ) | const |
Save an homography in a file. The load() function allows then to read and set the homography from this file.
Definition at line 152 of file vpHomography.cpp.
References vpException::ioError.
|
inlinestaticinherited |
Save an array in a YAML-formatted file.
| filename | : absolute file name. |
| A | : array to be saved in the file. |
| header | : optional lines that will be saved at the beginning of the file. Should be YAML-formatted and will adapt to the indentation if any. |
Here is an example of outputs.
Content of matrix.yml:
Content of matrixIndent.yml:
Definition at line 972 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
inlineinherited |
Return the number of elements of the 2D array.
Definition at line 349 of file vpArray2D.h.
Compute the transpose of the array.
Definition at line 648 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
related |
Insert array B in array A at the given position.
| A | : Main array. |
| B | : Array to insert. |
| C | : Result array. |
| r | : Index of the row where to insert array B. |
| c | : Index of the column where to insert array B. |
Definition at line 1096 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
related |
Definition at line 1351 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
related |
Definition at line 1313 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
related |
Definition at line 1332 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
related |
This function performs generalized matrix multiplication: D = alpha*op(A)*op(B) + beta*op(C), where op(X) is X or X^T. Operation on A, B and C matrices is described by enumeration vpGEMMmethod().
For example, to compute D = alpha*A^T*B^T+beta*C we need to call :
If C is not used, vpGEMM must be called using an empty array null. Thus to compute D = alpha*A^T*B, we have to call:
| vpException::incorrectMatrixSizeError | if the sizes of the matrices do not allow the operations. |
| A | : An array that could be a vpMatrix. |
| B | : An array that could be a vpMatrix. |
| alpha | : A scalar. |
| C | : An array that could be a vpMatrix. |
| beta | : A scalar. |
| D | : The resulting array that could be a vpMatrix. |
| ops | : A scalar describing operation applied on the matrices. Possible values are the one defined in vpGEMMmethod(): VP_GEMM_A_T, VP_GEMM_B_T, VP_GEMM_C_T. |
|
related |
Enumeration of the operations applied on matrices in vpGEMM() function.
Operations are :
|
protectedinherited |
Number of columns in the array.
Definition at line 1103 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
inherited |
Address of the first element of the data array.
Definition at line 148 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
protectedinherited |
Current array size (rowNum * colNum)
Definition at line 1107 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
protectedinherited |
Number of rows in the array.
Definition at line 1101 of file vpArray2D.h.
|
protectedinherited |
Address of the first element of each rows.
Definition at line 1105 of file vpArray2D.h.