Example of a complex non-linear use-case of the Unscented Kalman Filter (UKF). The system we are interested in is a 4-wheel robot, moving at a low velocity. As such, it can be modeled using a bicycle model.
Some noise is added to the measurement vector to simulate measurements which are not perfect.
The mean of several angles must be computed in the Unscented Transform. The definition we chose to use is the following:
As the Unscented Transform uses a weighted mean, the actual implementation of the weighted mean of several angles is the following:
Additionally, the addition and subtraction of angles must be carefully done, as the result must stay in the interval ![$[- \pi ; \pi ]$](form_1713.png) or
or ![$[0 ; 2 \pi ]$](form_1714.png) . We decided to use the interval
. We decided to use the interval ![$[- \pi ; \pi ]$](form_1713.png) .
.
#include <iostream>
#include <visp3/core/vpUKSigmaDrawerMerwe.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpUnscentedKalman.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpConfig.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpGaussRand.h>
#ifdef VISP_HAVE_DISPLAY
#include <visp3/gui/vpPlot.h>
#endif
#if (VISP_CXX_STANDARD >= VISP_CXX_STANDARD_11)
#ifdef ENABLE_VISP_NAMESPACE
#endif
namespace
{
double normalizeAngle(const double &angle)
{
double angleInMinPiPi = angleIn0to2pi;
if (angleInMinPiPi > M_PI) {
angleInMinPiPi -= 2. * M_PI;
}
return angleInMinPiPi;
}
vpColVector measurementMean(
const std::vector<vpColVector> &measurements,
const std::vector<double> &wm)
{
const unsigned int nbPoints = static_cast<unsigned int>(measurements.size());
const unsigned int sizeMeasurement = measurements[0].
size();
const unsigned int nbLandmarks = sizeMeasurement / 2;
std::vector<double> sumCos(nbLandmarks, 0.);
std::vector<double> sumSin(nbLandmarks, 0.);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < nbPoints; ++i) {
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < nbLandmarks; ++j) {
mean[2*j] += wm[i] * measurements[i][2*j];
sumCos[j] += wm[i] * std::cos(measurements[i][(2*j)+1]);
sumSin[j] += wm[i] * std::sin(measurements[i][(2*j)+1]);
}
}
for (unsigned int j = 0; j < nbLandmarks; ++j) {
mean[(2*j)+1] = std::atan2(sumSin[j], sumCos[j]);
}
return mean;
}
{
unsigned int nbMeasures = res.
size();
for (unsigned int i = 1; i < nbMeasures; i += 2) {
res[i] = normalizeAngle(res[i]);
}
return res;
}
{
add[2] = normalizeAngle(add[2]);
return add;
}
vpColVector stateMean(
const std::vector<vpColVector> &states,
const std::vector<double> &wm)
{
unsigned int nbPoints = static_cast<unsigned int>(states.size());
double sumCos = 0.;
double sumSin = 0.;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < nbPoints; ++i) {
mean[0] += wm[i] * states[i][0];
mean[1] += wm[i] * states[i][1];
sumCos += wm[i] * std::cos(states[i][2]);
sumSin += wm[i] * std::sin(states[i][2]);
}
mean[2] = std::atan2(sumSin, sumCos);
return mean;
}
{
res[2] = normalizeAngle(res[2]);
return res;
}
{
return x;
}
std::vector<vpColVector> generateTurnCommands(const double &v, const double &angleStart, const double &angleStop, const unsigned int &nbSteps)
{
std::vector<vpColVector> cmds;
double dTheta =
vpMath::rad(angleStop - angleStart) /
static_cast<double>(nbSteps - 1);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < nbSteps; ++i) {
double theta =
vpMath::rad(angleStart) + dTheta *
static_cast<double>(i);
cmd[0] = v;
cmd[1] = theta;
cmds.push_back(cmd);
}
return cmds;
}
std::vector<vpColVector> generateCommands()
{
std::vector<vpColVector> cmds;
unsigned int nbSteps = 30;
double dv = (1.1 - 0.001) / static_cast<double>(nbSteps - 1);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < nbSteps; ++i) {
cmd[0] = 0.001 + static_cast<double>(i) * dv;
cmd[1] = 0.;
cmds.push_back(cmd);
}
double lastLinearVelocity = cmds[cmds.size() -1][0];
std::vector<vpColVector> leftTurnCmds = generateTurnCommands(lastLinearVelocity, 0, 2, 15);
cmds.insert(cmds.end(), leftTurnCmds.begin(), leftTurnCmds.end());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {
cmds.push_back(cmds[cmds.size() -1]);
}
lastLinearVelocity = cmds[cmds.size() -1][0];
std::vector<vpColVector> rightTurnCmds = generateTurnCommands(lastLinearVelocity, 2, -2, 15);
cmds.insert(cmds.end(), rightTurnCmds.begin(), rightTurnCmds.end());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 200; ++i) {
cmds.push_back(cmds[cmds.size() -1]);
}
lastLinearVelocity = cmds[cmds.size() -1][0];
leftTurnCmds = generateTurnCommands(lastLinearVelocity, -2, 0, 15);
cmds.insert(cmds.end(), leftTurnCmds.begin(), leftTurnCmds.end());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 150; ++i) {
cmds.push_back(cmds[cmds.size() -1]);
}
lastLinearVelocity = cmds[cmds.size() -1][0];
leftTurnCmds = generateTurnCommands(lastLinearVelocity, 0, 1, 25);
cmds.insert(cmds.end(), leftTurnCmds.begin(), leftTurnCmds.end());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < 150; ++i) {
cmds.push_back(cmds[cmds.size() -1]);
}
return cmds;
}
}
{
public:
: m_w(w)
{ }
{
double heading = x[2];
double vel = u[0];
double steeringAngle = u[1];
double distance = vel * dt;
if (std::abs(steeringAngle) > 0.001) {
double beta = (distance / m_w) * std::tan(steeringAngle);
double radius = m_w / std::tan(steeringAngle);
double sinh = std::sin(heading);
double sinhb = std::sin(heading + beta);
double cosh = std::cos(heading);
double coshb = std::cos(heading + beta);
motion[0] = -radius * sinh + radius * sinhb;
motion[1] = radius * cosh - radius * coshb;
motion[2] = beta;
return motion;
}
else {
motion[0] = distance * std::cos(heading);
motion[1] = distance * std::sin(heading);
motion[2] = 0.;
return motion;
}
}
{
newX[2] = normalizeAngle(newX[2]);
return newX;
}
private:
double m_w;
};
{
public:
vpLandmarkMeasurements(
const double &x,
const double &y,
const double &range_std,
const double &rel_angle_std)
: m_x(x)
, m_y(y)
, m_rngRange(range_std, 0., 4224)
, m_rngRelativeAngle(rel_angle_std, 0., 2112)
{ }
{
double dx = m_x - chi[0];
double dy = m_y - chi[1];
meas[0] = std::sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
meas[1] = normalizeAngle(std::atan2(dy, dx) - chi[2]);
return meas;
}
{
double dx = m_x - pos[0];
double dy = m_y - pos[1];
double range = std::sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy);
double orientation = normalizeAngle(std::atan2(dy, dx) - pos[2]);
measurements[0] = range;
measurements[1] = orientation;
return measurements;
}
{
measurementsNoisy[0] += m_rngRange();
measurementsNoisy[1] += m_rngRelativeAngle();
measurementsNoisy[1] = normalizeAngle(measurementsNoisy[1]);
return measurementsNoisy;
}
private:
double m_x;
double m_y;
};
{
public:
: m_landmarks(landmarks)
{ }
{
unsigned int nbLandmarks = static_cast<unsigned int>(m_landmarks.size());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < nbLandmarks; ++i) {
vpColVector landmarkMeas = m_landmarks[i].state_to_measurement(chi);
measurements[2*i] = landmarkMeas[0];
measurements[(2*i) + 1] = landmarkMeas[1];
}
return measurements;
}
{
unsigned int nbLandmarks = static_cast<unsigned int>(m_landmarks.size());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < nbLandmarks; ++i) {
vpColVector landmarkMeas = m_landmarks[i].measureGT(pos);
measurements[2*i] = landmarkMeas[0];
measurements[(2*i) + 1] = landmarkMeas[1];
}
return measurements;
}
{
unsigned int nbLandmarks = static_cast<unsigned int>(m_landmarks.size());
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < nbLandmarks; ++i) {
vpColVector landmarkMeas = m_landmarks[i].measureWithNoise(pos);
measurements[2*i] = landmarkMeas[0];
measurements[(2*i) + 1] = landmarkMeas[1];
}
return measurements;
}
private:
std::vector<vpLandmarkMeasurements> m_landmarks;
};
int main(const int argc, const char *argv[])
{
bool opt_useDisplay = true;
for (int i = 1; i < argc; ++i) {
std::string arg(argv[i]);
if (arg == "-d") {
opt_useDisplay = false;
}
else if ((arg == "-h") || (arg == "--help")) {
std::cout << "SYNOPSIS" << std::endl;
std::cout << " " << argv[0] << " [-d][-h]" << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl << std::endl;
std::cout << "DETAILS" << std::endl;
std::cout << " -d" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Deactivate display." << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << " -h, --help" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
}
const double dt = 0.1;
const double step = 1.;
const double sigmaRange = 0.3;
const double wheelbase = 0.5;
const std::vector<vpLandmarkMeasurements> landmarks = {
vpLandmarkMeasurements(5, 10, sigmaRange, sigmaBearing)
const unsigned int nbLandmarks = static_cast<unsigned int>(landmarks.size());
std::vector<vpColVector> cmds = generateCommands();
const unsigned int nbCmds = static_cast<unsigned int>(cmds.size());
std::shared_ptr<vpUKSigmaDrawerAbstract> drawer = std::make_shared<vpUKSigmaDrawerMerwe>(3, 0.1, 2., 0, stateResidual, stateAdd);
R1landmark[0][0] = sigmaRange*sigmaRange;
R1landmark[1][1] = sigmaBearing*sigmaBearing;
vpMatrix R(2*nbLandmarks, 2 * nbLandmarks);
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < nbLandmarks; ++i) {
R.insert(R1landmark, 2*i, 2*i);
}
const double processVariance = 0.0001;
Q = Q * processVariance;
P0.eye(3);
P0[0][0] = 0.1;
P0[1][1] = 0.1;
P0[2][2] = 0.05;
X0[0] = 2.;
X0[1] = 6.;
X0[2] = 0.3;
using std::placeholders::_1;
using std::placeholders::_2;
using std::placeholders::_3;
ukf.init(X0, P0);
ukf.setCommandStateFunction(bx);
ukf.setMeasurementMeanFunction(measurementMean);
ukf.setMeasurementResidualFunction(measurementResidual);
ukf.setStateAddFunction(stateAdd);
ukf.setStateMeanFunction(stateMean);
ukf.setStateResidualFunction(stateResidual);
#ifdef VISP_HAVE_DISPLAY
if (opt_useDisplay) {
plot->
setTitle(0,
"Position of the robot");
plot->
setUnitX(0,
"Position along x(m)");
plot->
setUnitY(0,
"Position along y (m)");
}
#endif
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < nbCmds; ++i) {
robot_pos = robot.move(cmds[i], robot_pos, dt / step);
if (i % static_cast<int>(step) == 0) {
ukf.filter(z, dt, cmds[i]);
#ifdef VISP_HAVE_DISPLAY
if (opt_useDisplay) {
plot->
plot(0, 1, Xest[0], Xest[1]);
}
#endif
}
#ifdef VISP_HAVE_DISPLAY
if (opt_useDisplay) {
plot->
plot(0, 0, robot_pos[0], robot_pos[1]);
}
#endif
}
if (opt_useDisplay) {
std::cout << "Press Enter to quit..." << std::endl;
std::cin.get();
}
#ifdef VISP_HAVE_DISPLAY
if (opt_useDisplay) {
delete plot;
}
#endif
vpColVector finalError = grid.state_to_measurement(ukf.getXest()) - grid.measureGT(robot_pos);
const double maxError = 0.3;
std::cerr <<
"Error: max tolerated error = " << maxError <<
", final error = " << finalError.
frobeniusNorm() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
#else
int main()
{
std::cout << "This example is only available if you compile ViSP in C++11 standard or higher." << std::endl;
return 0;
}
#endif
unsigned int size() const
Return the number of elements of the 2D array.
Class that approximates a 4-wheel robot using a bicycle model.
vpColVector computeMotion(const vpColVector &u, const vpColVector &x, const double &dt)
Models the effect of the command on the state model.
Implementation of column vector and the associated operations.
double frobeniusNorm() const
Class for generating random number with normal probability density.
Class that permits to convert the position + heading of the 4-wheel robot into measurements from a la...
Class that represent a grid of landmarks that measure the distance and relative orientation of the 4-...
vpColVector state_to_measurement(const vpColVector &chi)
Convert the prior of the UKF into the measurement space.
static double rad(double deg)
static float modulo(const float &value, const float &modulo)
Gives the rest of value divided by modulo when the quotient can only be an integer.
Implementation of a matrix and operations on matrices.
This class enables real time drawing of 2D or 3D graphics. An instance of the class open a window whi...
void initGraph(unsigned int graphNum, unsigned int curveNbr)
void setUnitY(unsigned int graphNum, const std::string &unity)
void setLegend(unsigned int graphNum, unsigned int curveNum, const std::string &legend)
void plot(unsigned int graphNum, unsigned int curveNum, double x, double y)
void setUnitX(unsigned int graphNum, const std::string &unitx)
void setTitle(unsigned int graphNum, const std::string &title)
std::function< vpColVector(const vpColVector &, const vpColVector &, const double &)> vpCommandStateFunction
Command model function, which projects effect of the command on the state, when the effect of the com...
std::function< vpColVector(const vpColVector &)> vpMeasurementFunction
Measurement function, which converts the prior points in the measurement space. The argument is a poi...
std::function< vpColVector(const vpColVector &, const double &)> vpProcessFunction
Process model function, which projects the sigma points forward in time. The first argument is a sigm...


![]()
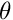 is the heading of the robot.
is the heading of the robot.![]() corresponds to the distance and relative orientation of the robot with different landmarks. Be
corresponds to the distance and relative orientation of the robot with different landmarks. Be ![]() and
and ![]() the position of the
the position of the ![]() landmark along the x and y axis, the measurement vector can be written as:
landmark along the x and y axis, the measurement vector can be written as: ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]() is the weight associated to the
is the weight associated to the ![]() measurements for the weighted mean.
measurements for the weighted mean.![]() or
or ![]() . We decided to use the interval
. We decided to use the interval ![]() .
.