 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.6.1 under development (2025-03-06)
|
 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.6.1 under development (2025-03-06)
|
#include <visp3/robot/vpViper850.h>
 Inheritance diagram for vpViper850:
Inheritance diagram for vpViper850:Public Types | |
| enum | vpToolType { TOOL_MARLIN_F033C_CAMERA , TOOL_PTGREY_FLEA2_CAMERA , TOOL_SCHUNK_GRIPPER_CAMERA , TOOL_GENERIC_CAMERA , TOOL_CUSTOM } |
Public Member Functions | |
| vpViper850 () | |
Inherited functionalities from vpViper850 | |
| void | init (void) |
| void | init (const std::string &camera_extrinsic_parameters) |
| void | init (vpViper850::vpToolType tool, vpCameraParameters::vpCameraParametersProjType projModel=vpCameraParameters::perspectiveProjWithoutDistortion) |
| void | init (vpViper850::vpToolType tool, const std::string &filename) |
| void | init (vpViper850::vpToolType tool, const vpHomogeneousMatrix &eMc_) |
| vpCameraParameters::vpCameraParametersProjType | getCameraParametersProjType () const |
| void | getCameraParameters (vpCameraParameters &cam, const unsigned int &image_width, const unsigned int &image_height) const |
| void | getCameraParameters (vpCameraParameters &cam, const vpImage< unsigned char > &I) const |
| void | getCameraParameters (vpCameraParameters &cam, const vpImage< vpRGBa > &I) const |
| vpToolType | getToolType () const |
| void | parseConfigFile (const std::string &filename) |
Protected Member Functions Inherited from vpViper650 | |
| vpToolType | tool_current |
| vpCameraParameters::vpCameraParametersProjType | projModel |
| void | setToolType (vpViper850::vpToolType tool) |
Modelization of the ADEPT Viper 850 robot.
The model of the robot is the following:
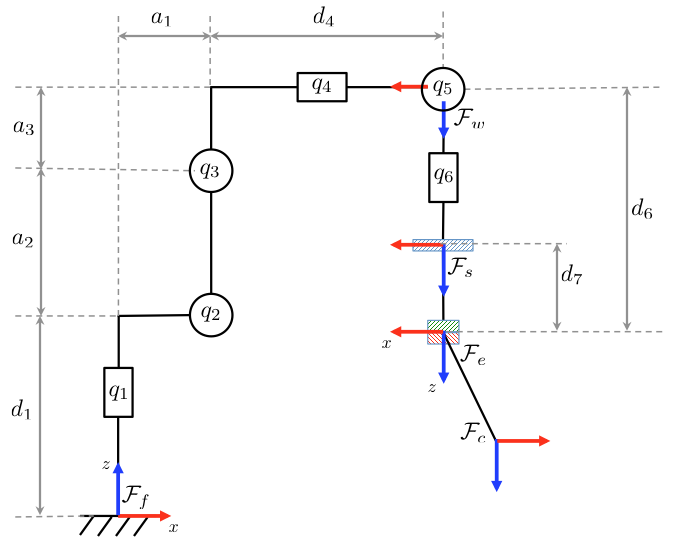
The non modified Denavit-Hartenberg representation of the robot is given in the table below, where ![]() are the variable joint positions.
are the variable joint positions.
![\[ \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline Joint & $a_i$ & $d_i$ & $\alpha_i$ & $\theta_i$ \\ \hline 1 & $a_1$ & $d_1$ & $-\pi/2$ & $q_1^*$ \\ 2 & $a_2$ & 0 & 0 & $q_2^*$ \\ 3 & $a_3$ & 0 & $-\pi/2$ & $q_3^* - \pi$ \\ 4 & 0 & $d_4$ & $\pi/2$ & $q_4^*$ \\ 5 & 0 & 0 & $-\pi/2$ & $q_5^*$ \\ 6 & 0 & 0 & 0 & $q_6^*-\pi$ \\ 7 & 0 & $d_6$ & 0 & 0 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \]](form_687.png)
In this modelization, different frames have to be considered.
Definition at line 94 of file vpViper850.h.
List of possible tools that can be attached to the robot end-effector.
Definition at line 119 of file vpViper850.h.
| vpViper850::vpViper850 | ( | ) |
Default constructor. Sets the specific parameters like the Denavit-Hartenberg parameters.
Definition at line 100 of file vpViper850.cpp.
References vpViper::a1, vpViper::a2, vpViper::a3, vpViper::c56, vpViper::d1, vpViper::d4, vpViper::d6, init(), vpViper::joint_max, vpViper::joint_min, and vpMath::rad().
|
inherited |
Get the geometric transformation between the camera frame and the end-effector frame. This transformation is constant and correspond to the extrinsic camera parameters estimated by calibration.
| cMe | : Transformation between the camera frame and the end-effector frame. |
Definition at line 921 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::eMc, and vpHomogeneousMatrix::inverse().
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::get_cMe(), vpRobotViper650::get_cMe(), vpRobotViper850::get_cMe(), vpSimulatorViper850::get_cVe(), vpRobotViper650::get_cVe(), vpRobotViper850::get_cVe(), and vpViper::get_cVe().
|
inherited |
Get the twist transformation ![]() from camera frame to end-effector frame. This transformation allows to compute a velocity expressed in the end-effector frame into the camera frame.
from camera frame to end-effector frame. This transformation allows to compute a velocity expressed in the end-effector frame into the camera frame.
![]()
| cVe | : Twist transformation |
Definition at line 937 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpVelocityTwistMatrix::buildFrom(), and vpViper::get_cMe().
|
inherited |
Get the robot jacobian ![]() which gives the velocity of the origin of the end-effector frame expressed in end-effector frame.
which gives the velocity of the origin of the end-effector frame expressed in end-effector frame.
![]()
| q | : A six-dimension vector that contains the joint positions of the robot expressed in radians. |
| eJe | : Robot jacobian |
Definition at line 969 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpHomogeneousMatrix::extract(), vpViper::get_fJw(), vpViper::get_fMw(), vpViper::get_wMe(), vpHomogeneousMatrix::inverse(), vpRotationMatrix::inverse(), and vpTranslationVector::skew().
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::computeArticularVelocity(), vpRobotViper650::get_eJe(), vpRobotViper850::get_eJe(), vpSimulatorViper850::get_eJe(), and vpSimulatorViper850::getVelocity().
|
inherited |
Get the geometric transformation between the end-effector frame and the camera frame. This transformation is constant and correspond to the extrinsic camera parameters estimated by calibration.
| eMc_ | : Transformation between the the end-effector frame and the camera frame. |
Definition at line 893 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::eMc.
Referenced by vpViper::getInverseKinematics().
|
inherited |
Get the geometric transformation between the end-effector frame and the force/torque sensor frame. This transformation is constant.
| eMs | : Transformation between the the end-effector frame and the force/torque sensor frame. |
Definition at line 904 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::d7, and vpHomogeneousMatrix::eye().
|
inherited |
Get the robot jacobian ![]() which gives the velocity of the origin of the end-effector frame expressed in the robot reference frame also called fix frame.
which gives the velocity of the origin of the end-effector frame expressed in the robot reference frame also called fix frame.
![]()
| q | : A six-dimension vector that contains the joint positions of the robot expressed in radians. |
| fJe | : Robot jacobian |
Definition at line 1158 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpHomogeneousMatrix::extract(), vpViper::get_fJw(), vpViper::get_fMw(), vpViper::get_wMe(), and vpHomogeneousMatrix::inverse().
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::computeArticularVelocity(), vpRobotViper650::get_fJe(), vpRobotViper850::get_fJe(), vpSimulatorViper850::get_fJe(), and vpSimulatorViper850::getVelocity().
|
inherited |
Get the robot jacobian ![]() which express the velocity of the origin of the wrist frame in the robot reference frame also called fix frame.
which express the velocity of the origin of the wrist frame in the robot reference frame also called fix frame.
![\[ {^f}J_w = \left(\begin{array}{cccccc} J_{11} & J_{12} & J_{13} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ J_{21} & J_{22} & J_{23} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & J_{32} & J_{33} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & -s1 & -s1 & c1s23 & J_{45} & J_{46} \\ 0 & c1 & c1 & s1s23 & J_{55} & J_{56} \\ 1 & 0 & 0 & c23 & s23s4 & J_{56} \\ \end{array} \right) \]](form_777.png)
with
![\[ \begin{array}{l} J_{11} = -s1(-c23a3+s23d4+a1+a2c2) \\ J_{21} = c1(-c23a3+s23d4+a1+a2c2) \\ J_{12} = c1(s23a3+c23d4-a2s2) \\ J_{22} = s1(s23a3+c23d4-a2s2) \\ J_{32} = c23a3-s23d4-a2c2 \\ J_{13} = c1(a3(s2c3+c2s3)+(-s2s3+c2c3)d4)\\ J_{23} = s1(a3(s2c3+c2s3)+(-s2s3+c2c3)d4)\\ J_{33} = -a3(s2s3-c2c3)-d4(s2c3+c2s3)\\ J_{45} = -c23c1s4-s1c4\\ J_{55} = c1c4-c23s1s4\\ J_{46} = (c1c23c4-s1s4)s5+c1s23c5\\ J_{56} = (s1c23c4+c1s4)s5+s1s23c5\\ J_{66} = -s23c4s5+c23c5\\ \end{array} \]](form_778.png)
| q | : A six-dimension vector that contains the joint positions of the robot expressed in radians. |
| fJw | : Robot jacobian |
Definition at line 1053 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::a1, vpViper::a2, vpViper::a3, vpViper::d4, and vpArray2D< Type >::resize().
Referenced by vpViper::get_eJe(), and vpViper::get_fJe().
|
inherited |
Compute the forward kinematics (direct geometric model) as an homogeneous matrix.
By forward kinematics we mean here the position and the orientation of the camera relative to the base frame given the joint positions of all the six joints.
![]()
This method is the same than getForwardKinematics(const vpColVector & q).
| q | : Vector of six joint positions expressed in radians. |
Definition at line 605 of file vpViper.cpp.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), vpViper::getForwardKinematics(), vpRobotViper650::getPosition(), vpRobotViper850::getPosition(), vpSimulatorViper850::getPosition(), vpRobotViper650::getVelocity(), vpRobotViper850::getVelocity(), vpRobotViper650::setPosition(), vpRobotViper850::setPosition(), and vpSimulatorViper850::setPosition().
|
inherited |
Compute the forward kinematics (direct geometric model) as an homogeneous matrix.
By forward kinematics we mean here the position and the orientation of the camera relative to the base frame given the six joint positions.
![]()
| q | : Vector of six joint positions expressed in radians. |
| fMc | The homogeneous matrix |
Definition at line 634 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::eMc, and vpViper::get_fMe().
|
inherited |
Compute the forward kinematics (direct geometric model) as an homogeneous matrix ![]() .
.
By forward kinematics we mean here the position and the orientation of the end effector with respect to the base frame given the motor positions of all the six joints.
![]()
with
![\[ \begin{array}{l} r_{11} = c1(c23(c4c5c6-s4s6)-s23s5c6)-s1(s4c5c6+c4s6) \\ r_{21} = -s1(c23(-c4c5c6+s4s6)+s23s5c6)+c1(s4c5c6+c4s6) \\ r_{31} = s23(s4s6-c4c5c6)-c23s5c6 \\ \\ r_{12} = -c1(c23(c4c5s6+s4c6)-s23s5s6)+s1(s4c5s6-c4c6)\\ r_{22} = -s1(c23(c4c5s6+s4c6)-s23s5s6)-c1(s4c5s6-c4c6)\\ r_{32} = s23(c4c5s6+s4c6)+c23s5s6\\ \\ r_{13} = c1(c23c4s5+s23c5)-s1s4s5\\ r_{23} = s1(c23c4s5+s23c5)+c1s4s5\\ r_{33} = -s23c4s5+c23c5\\ \\ t_x = c1(c23(c4s5d6-a3)+s23(c5d6+d4)+a1+a2c2)-s1s4s5d6\\ t_y = s1(c23(c4s5d6-a3)+s23(c5d6+d4)+a1+a2c2)+c1s4s5d6\\ t_z = s23(a3-c4s5d6)+c23(c5d6+d4)-a2s2+d1\\ \end{array} \]](form_770.png)
| q | : A 6-dimension vector that contains the 6 joint positions expressed in radians. |
| fMe | The homogeneous matrix |
Note that this transformation can also be computed by considering the wrist frame ![]() .
.
Definition at line 724 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::a1, vpViper::a2, vpViper::a3, vpViper::d1, vpViper::d4, and vpViper::d6.
Referenced by vpViper::get_fMc(), vpRobotViper650::getVelocity(), and vpRobotViper850::getVelocity().
|
inherited |
Compute the transformation between the fix frame and the wrist frame. The wrist frame is located on the intersection of the 3 last rotations.
| q | : A 6-dimension vector that contains the 6 joint positions expressed in radians. |
| fMw | The homogeneous matrix corresponding to the transformation between the fix frame and the wrist frame (fMw). |
![]()
with
![\[ \begin{array}{l} r_{11} = c1(c23(c4c5c6-s4s6)-s23s5c6)-s1(s4c5c6+c4s6) \\ r_{21} = -s1(c23(-c4c5c6+s4s6)+s23s5c6)+c1(s4c5c6+c4s6) \\ r_{31} = s23(s4s6-c4c5c6)-c23s5c6 \\ \\ r_{12} = -c1(c23(c4c5s6+s4c6)-s23s5s6)+s1(s4c5s6-c4c6)\\ r_{22} = -s1(c23(c4c5s6+s4c6)-s23s5s6)-c1(s4c5s6-c4c6)\\ r_{32} = s23(c4c5s6+s4c6)+c23s5s6\\ \\ r_{13} = c1(c23c4s5+s23c5)-s1s4s5\\ r_{23} = s1(c23c4s5+s23c5)+c1s4s5\\ r_{33} = -s23c4s5+c23c5\\ \\ t_x = c1(-c23a3+s23d4+a1+a2c2)\\ t_y = s1(-c23a3+s23d4+a1+a2c2)\\ t_z = s23a3+c23d4-a2s2+d1\\ \end{array} \]](form_773.png)
Definition at line 814 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::a1, vpViper::a2, vpViper::a3, vpViper::d1, and vpViper::d4.
Referenced by vpViper::get_eJe(), and vpViper::get_fJe().
|
inherited |
Return the transformation between the wrist frame and the end-effector. The wrist frame is located on the intersection of the 3 last rotations.
| wMe | The homogeneous matrix corresponding to the transformation between the wrist frame and the end-effector frame (wMe). |
Definition at line 873 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::d6, and vpHomogeneousMatrix::eye().
Referenced by vpViper::get_eJe(), vpViper::get_fJe(), and vpViper::getInverseKinematics().
| void vpViper850::getCameraParameters | ( | vpCameraParameters & | cam, |
| const unsigned int & | image_width, | ||
| const unsigned int & | image_height | ||
| ) | const |
Get the current intrinsic camera parameters obtained by calibration.
| cam | : In output, camera parameters to fill. |
| image_width | : Image width used to compute camera calibration. |
| image_height | : Image height used to compute camera calibration. |
The code below shows how to get the camera parameters of the camera attached to the robot.
| vpRobotException::readingParametersError | : If the camera parameters are not found. |
Definition at line 561 of file vpViper850.cpp.
References vpException::badValue, CONST_CAMERA_FILENAME, CONST_GENERIC_CAMERA_NAME, CONST_MARLIN_F033C_CAMERA_NAME, CONST_PTGREY_FLEA2_CAMERA_NAME, CONST_SCHUNK_GRIPPER_CAMERA_NAME, getToolType(), vpCameraParameters::initPersProjWithDistortion(), vpCameraParameters::initPersProjWithoutDistortion(), vpException::notImplementedError, vpXmlParserCamera::parse(), vpCameraParameters::perspectiveProjWithDistortion, vpCameraParameters::perspectiveProjWithoutDistortion, projModel, vpCameraParameters::ProjWithKannalaBrandtDistortion, vpRobotException::readingParametersError, vpXmlParserCamera::SEQUENCE_OK, TOOL_CUSTOM, TOOL_GENERIC_CAMERA, TOOL_MARLIN_F033C_CAMERA, TOOL_PTGREY_FLEA2_CAMERA, TOOL_SCHUNK_GRIPPER_CAMERA, vpERROR_TRACE, and vpTRACE.
Referenced by getCameraParameters().
| void vpViper850::getCameraParameters | ( | vpCameraParameters & | cam, |
| const vpImage< unsigned char > & | I | ||
| ) | const |
Get the current intrinsic camera parameters obtained by calibration.
| cam | : In output, camera parameters to fill. |
| I | : A B&W image send by the current camera in use. |
| vpRobotException::readingParametersError | : If the camera parameters are not found. |
Definition at line 772 of file vpViper850.cpp.
References getCameraParameters(), vpImage< Type >::getHeight(), and vpImage< Type >::getWidth().
| void vpViper850::getCameraParameters | ( | vpCameraParameters & | cam, |
| const vpImage< vpRGBa > & | I | ||
| ) | const |
Get the current intrinsic camera parameters obtained by calibration.
| cam | : In output, camera parameters to fill. |
| I | : A color image send by the current camera in use. |
| vpRobotException::readingParametersError | : If the camera parameters are not found. |
Definition at line 841 of file vpViper850.cpp.
References getCameraParameters(), vpImage< Type >::getHeight(), and vpImage< Type >::getWidth().
|
inline |
Get the current camera model projection type.
Definition at line 144 of file vpViper850.h.
|
inherited |
Return the coupling factor between join 5 and joint 6.
This factor should be only useful when motor positions are considered. Since the positions returned by the robot are joint positions which takes into account the coupling factor, it has not to be considered in the modelization of the robot.
Definition at line 1219 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::c56.
|
inherited |
Compute the forward kinematics (direct geometric model) as an homogeneous matrix.
By forward kinematics we mean here the position and the orientation of the camera relative to the base frame given the six joint positions.
This method is the same than get_fMc(const vpColVector & q).
| q | : A six dimension vector corresponding to the robot joint positions expressed in radians. |
Definition at line 119 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::get_fMc().
|
inherited |
Compute the inverse kinematics (inverse geometric model).
By inverse kinematics we mean here the six joint values given the position and the orientation of the camera frame relative to the base frame.
| fMc | : Homogeneous matrix |
| q | : In input, a six dimension vector corresponding to the current joint positions expressed in radians. In output, the solution of the inverse kinematics, ie. the joint positions corresponding to |
| verbose | : Add extra printings. |
The code below shows how to compute the inverse geometric model:
Definition at line 568 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::get_eMc(), vpViper::get_wMe(), vpViper::getInverseKinematicsWrist(), and vpHomogeneousMatrix::inverse().
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::initialiseCameraRelativeToObject(), vpRobotViper650::setPosition(), vpRobotViper850::setPosition(), and vpSimulatorViper850::setPosition().
|
inherited |
Compute the inverse kinematics (inverse geometric model).
By inverse kinematics we mean here the six joint values given the position and the orientation of the camera frame relative to the base frame.
| fMw | : Homogeneous matrix |
| q | : In input, a six dimension vector corresponding to the current joint positions expressed in radians. In output, the solution of the inverse kinematics, ie. the joint positions corresponding to |
| verbose | : Add extra printings. |
The code below shows how to compute the inverse geometric model:
Definition at line 220 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::a1, vpViper::a2, vpViper::a3, vpViper::d1, vpViper::d4, vpArray2D< Type >::getRows(), vpViper::njoint, vpMath::rad(), vpColVector::resize(), and vpMath::sqr().
Referenced by vpViper::getInverseKinematics().
|
inherited |
Get maximal joint values.
Definition at line 1207 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::joint_max.
|
inherited |
Get minimal joint values.
Definition at line 1198 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpViper::joint_min.
|
inline |
Get the current tool type.
Definition at line 152 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::getCameraParameters(), and getCameraParameters().
| void vpViper850::init | ( | const std::string & | camera_extrinsic_parameters | ) |
Read files containing the constant parameters related to the robot tools in order to set the end-effector to tool transformation.
| camera_extrinsic_parameters | : Filename containing the camera extrinsic parameters. |
Definition at line 149 of file vpViper850.cpp.
References parseConfigFile().
| void vpViper850::init | ( | void | ) |
Initialize the robot with the default tool vpViper850::defaultTool.
Definition at line 134 of file vpViper850.cpp.
References defaultTool.
Referenced by vpRobotViper850::init(), init(), and vpViper850().
| void vpViper850::init | ( | vpViper850::vpToolType | tool, |
| const std::string & | filename | ||
| ) |
Set the type of tool attached to the robot and transformation between the end-effector and the tool ( ![]() ). This last parameter is loaded from a file.
). This last parameter is loaded from a file.
| tool | : Type of tool in use. |
| filename | : Path of the configuration file containing the transformation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame. |
The configuration file should have the form below:
Definition at line 381 of file vpViper850.cpp.
References parseConfigFile(), and setToolType().
| void vpViper850::init | ( | vpViper850::vpToolType | tool, |
| const vpHomogeneousMatrix & | eMc_ | ||
| ) |
Set the type of tool attached to the robot and the transformation between the end-effector and the tool ( ![]() ).
).
| tool | : Type of tool in use. |
| eMc_ | : Homogeneous matrix representation of the transformation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame. |
Definition at line 402 of file vpViper850.cpp.
References vpViper::set_eMc(), and setToolType().
| void vpViper850::init | ( | vpViper850::vpToolType | tool, |
| vpCameraParameters::vpCameraParametersProjType | proj_model = vpCameraParameters::perspectiveProjWithoutDistortion |
||
| ) |
Set the constant parameters related to the robot kinematics and to the end-effector to camera transformation ( ![]() ) corresponding to the camera extrinsic parameters. These last parameters depend on the camera and projection model in use and are loaded from predefined files or parameters.
) corresponding to the camera extrinsic parameters. These last parameters depend on the camera and projection model in use and are loaded from predefined files or parameters.
| tool | : Camera in use. |
| proj_model | : Projection model of the camera. |
Definition at line 178 of file vpViper850.cpp.
References vpException::badValue, vpHomogeneousMatrix::buildFrom(), CONST_EMC_GENERIC_WITH_DISTORTION_FILENAME, CONST_EMC_GENERIC_WITHOUT_DISTORTION_FILENAME, CONST_EMC_MARLIN_F033C_WITH_DISTORTION_FILENAME, CONST_EMC_MARLIN_F033C_WITHOUT_DISTORTION_FILENAME, CONST_EMC_PTGREY_FLEA2_WITH_DISTORTION_FILENAME, CONST_EMC_PTGREY_FLEA2_WITHOUT_DISTORTION_FILENAME, CONST_EMC_SCHUNK_GRIPPER_WITH_DISTORTION_FILENAME, CONST_EMC_SCHUNK_GRIPPER_WITHOUT_DISTORTION_FILENAME, vpViper::eMc, vpViper::erc, vpViper::etc, init(), vpException::notImplementedError, vpCameraParameters::perspectiveProjWithDistortion, vpCameraParameters::perspectiveProjWithoutDistortion, projModel, vpCameraParameters::ProjWithKannalaBrandtDistortion, vpMath::rad(), setToolType(), TOOL_CUSTOM, TOOL_GENERIC_CAMERA, TOOL_MARLIN_F033C_CAMERA, TOOL_PTGREY_FLEA2_CAMERA, TOOL_SCHUNK_GRIPPER_CAMERA, and vpERROR_TRACE.
| void vpViper850::parseConfigFile | ( | const std::string & | filename | ) |
This function gets the robot constant parameters from a file.
| filename | : File name containing the robot constant parameters, like the hand-to-eye transformation. |
Definition at line 416 of file vpViper850.cpp.
References vpRobotException::readingParametersError, and vpViper::set_eMc().
Referenced by init().
|
virtualinherited |
Set the geometric transformation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame (commonly a camera).
| eMc_ | : Transformation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame. |
Reimplemented in vpRobotViper850, and vpRobotViper650.
Definition at line 1229 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpRxyzVector::buildFrom(), vpViper::eMc, vpViper::erc, vpViper::etc, and vpHomogeneousMatrix::extract().
Referenced by vpViper650::init(), init(), vpViper650::parseConfigFile(), parseConfigFile(), vpRobotViper650::set_eMc(), and vpRobotViper850::set_eMc().
|
virtualinherited |
Set the geometric transformation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame (commonly a camera frame).
| etc_ | : Translation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame. |
| erc_ | : Rotation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame using the Euler angles in radians with the XYZ convention. |
Reimplemented in vpRobotViper850, and vpRobotViper650.
Definition at line 1247 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpHomogeneousMatrix::buildFrom(), vpViper::eMc, vpViper::erc, and vpViper::etc.
|
inlineprotected |
Set the current tool type.
Definition at line 161 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::init(), and init().
|
protectedinherited |
Definition at line 162 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), vpViper::get_fJw(), vpViper::get_fMe(), vpViper::get_fMw(), vpViper::getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpSimulatorViper850::singularityTest(), vpViper::vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850().
|
protectedinherited |
for joint 2
Definition at line 163 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), vpViper::get_fJw(), vpViper::get_fMe(), vpViper::get_fMw(), vpViper::getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpSimulatorViper850::singularityTest(), vpViper::vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850().
|
protectedinherited |
for joint 3
Definition at line 164 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), vpViper::get_fJw(), vpViper::get_fMe(), vpViper::get_fMw(), vpViper::getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpSimulatorViper850::singularityTest(), vpViper::vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850().
|
protectedinherited |
Mechanical coupling between joint 5 and joint 6.
Definition at line 168 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpViper::getCoupl56(), vpViper::vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850().
|
static |
Definition at line 108 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by getCameraParameters().
|
static |
Definition at line 107 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by init().
|
static |
Definition at line 106 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by init().
|
static |
Definition at line 101 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by init().
|
static |
Files where constant transformation between end-effector and camera frame are stored.
Definition at line 100 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by init().
|
static |
Definition at line 103 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by init().
|
static |
Definition at line 102 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by init().
|
static |
Definition at line 105 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by init().
|
static |
Definition at line 104 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by init().
|
static |
Definition at line 116 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by getCameraParameters().
|
static |
Name of the camera attached to the end-effector.
Definition at line 113 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::getCameraParameters(), and getCameraParameters().
|
static |
Definition at line 114 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::getCameraParameters(), and getCameraParameters().
|
static |
Definition at line 115 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by getCameraParameters().
|
protectedinherited |
for joint 1
Definition at line 162 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), vpViper::get_fMe(), vpViper::get_fMw(), vpViper::getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpViper::vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850().
|
protectedinherited |
for joint 4
Definition at line 165 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), vpViper::get_fJw(), vpViper::get_fMe(), vpViper::get_fMw(), vpViper::getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpSimulatorViper850::singularityTest(), vpViper::vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850().
|
protectedinherited |
for joint 6
Definition at line 166 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), vpViper::get_fMe(), vpViper::get_wMe(), vpViper::vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850().
|
protectedinherited |
for force/torque location
Definition at line 167 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpViper::get_eMs(), and vpViper::vpViper().
|
static |
Default tool attached to the robot end effector.
Definition at line 129 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpRobotViper850::init(), and init().
|
protectedinherited |
End effector to camera transformation.
Definition at line 156 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::computeArticularVelocity(), vpViper::get_cMe(), vpViper::get_eMc(), vpViper::get_fMc(), vpSimulatorViper850::getVelocity(), vpViper650::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), init(), vpViper::set_eMc(), and vpViper::vpViper().
|
protectedinherited |
Definition at line 159 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpRobotViper650::init(), vpViper650::init(), vpRobotViper850::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), init(), vpRobotViper650::set_eMc(), vpRobotViper850::set_eMc(), and vpViper::set_eMc().
|
protectedinherited |
Definition at line 158 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpRobotViper650::init(), vpViper650::init(), vpRobotViper850::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), init(), vpRobotViper650::set_eMc(), vpRobotViper850::set_eMc(), and vpViper::set_eMc().
|
protectedinherited |
Definition at line 171 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpViper::getJointMax(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpRobotViper650::init(), vpRobotViper850::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::isInJointLimit(), vpSimulatorViper850::setJointLimit(), vpSimulatorViper850::updateArticularPosition(), vpViper::vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850().
|
protectedinherited |
Definition at line 172 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpViper::getJointMin(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpRobotViper650::init(), vpRobotViper850::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::isInJointLimit(), vpSimulatorViper850::setJointLimit(), vpSimulatorViper850::updateArticularPosition(), vpViper::vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850().
|
staticinherited |
Number of joint.
Definition at line 153 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpRobotViper650::get_eJe(), vpRobotViper850::get_eJe(), vpRobotViper650::get_fJe(), vpRobotViper850::get_fJe(), vpRobotViper650::getDisplacement(), vpRobotViper850::getDisplacement(), vpViper::getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpRobotViper650::getPosition(), vpRobotViper850::getPosition(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpRobotViper650::readPosFile(), vpRobotViper850::readPosFile(), vpSimulatorViper850::readPosFile(), vpRobotViper650::setPosition(), vpRobotViper850::setPosition(), vpRobotViper650::setVelocity(), vpRobotViper850::setVelocity(), and vpViper::vpViper().
|
protected |
Definition at line 168 of file vpViper850.h.
Referenced by getCameraParameters(), vpRobotViper850::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), and init().
|
protected |
Current tool in use.
Definition at line 166 of file vpViper850.h.