 |
ViSP
2.8.0
|
 |
ViSP
2.8.0
|
#include <vpRobotCamera.h>
 Inheritance diagram for vpRobotCamera:
Inheritance diagram for vpRobotCamera:Public Types | |
| enum | vpRobotStateType { STATE_STOP, STATE_VELOCITY_CONTROL, STATE_POSITION_CONTROL, STATE_ACCELERATION_CONTROL } |
| enum | vpControlFrameType { REFERENCE_FRAME, ARTICULAR_FRAME, CAMERA_FRAME, MIXT_FRAME } |
Public Member Functions | |
| vpRobotCamera () | |
| virtual | ~vpRobotCamera () |
| void | get_cVe (vpVelocityTwistMatrix &cVe) |
| void | get_eJe (vpMatrix &eJe) |
| void | getPosition (vpHomogeneousMatrix &cMw) const |
| void | getPosition (const vpRobot::vpControlFrameType frame, vpColVector &q) |
| void | setPosition (const vpHomogeneousMatrix &cMw) |
| void | setVelocity (const vpRobot::vpControlFrameType frame, const vpColVector &v) |
| double | getSamplingTime () const |
| virtual void | setSamplingTime (const double &delta_t) |
| double | getMaxTranslationVelocity (void) const |
| double | getMaxRotationVelocity (void) const |
| vpColVector | getPosition (const vpRobot::vpControlFrameType frame) |
| virtual vpRobotStateType | getRobotState (void) |
| void | setMaxRotationVelocity (const double maxVr) |
| void | setMaxTranslationVelocity (const double maxVt) |
| virtual vpRobotStateType | setRobotState (const vpRobot::vpRobotStateType newState) |
| void | setVerbose (bool verbose) |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static vpColVector | saturateVelocities (const vpColVector &v_in, const vpColVector &v_max, bool verbose=false) |
Protected Member Functions | |
| vpControlFrameType | setRobotFrame (vpRobot::vpControlFrameType newFrame) |
| vpControlFrameType | getRobotFrame (void) |
Protected Attributes | |
| vpHomogeneousMatrix | cMw_ |
| double | delta_t_ |
| double | maxTranslationVelocity |
| double | maxRotationVelocity |
| int | nDof |
| vpMatrix | eJe |
| int | eJeAvailable |
| vpMatrix | fJe |
| int | fJeAvailable |
| int | areJointLimitsAvailable |
| double * | qmin |
| double * | qmax |
| bool | verbose_ |
Static Protected Attributes | |
| static const double | maxTranslationVelocityDefault = 0.2 |
| static const double | maxRotationVelocityDefault = 0.7 |
Class that defines the simplest robot: a free flying camera.
This free flying camera has 6 dof; 3 in translation and 3 in rotation. It evolves as a gentry robot with respect to a world frame. This class is similar to vpSimulatorCamera class except that here the position of the robot is provided as the transformation from camera frame to world frame; cMw. Since the position of the camera frame evolves, this representation is less intuitive than the one implemented in vpSimulatorCamera where the transformation from world to camera frame is considered; wMc.
For this particular simulated robot, the end-effector and camera frame are confused. That means that the cMe transformation is equal to identity.
The robot jacobian expressed in the end-effector frame 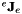 is also set to identity (see get_eJe()).
is also set to identity (see get_eJe()).
The following code shows how to control this robot in position and velocity.
Definition at line 110 of file vpRobotCamera.h.
|
inherited |
Robot control frames.
|
inherited |
| vpRobotCamera::vpRobotCamera | ( | ) |
Constructor.
Initialise the robot by a call to init().
Sampling time is set to 40 ms. To change it you should call setSamplingTime().
Robot jacobian expressed in the end-effector frame 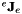 is set to identity (see get_eJe()).
is set to identity (see get_eJe()).
Definition at line 74 of file vpRobotCamera.cpp.
|
virtual |
Destructor.
Definition at line 106 of file vpRobotCamera.cpp.
| void vpRobotCamera::get_cVe | ( | vpVelocityTwistMatrix & | cVe | ) |
Get the twist transformation from camera frame to end-effector frame. This transformation allows to compute a velocity expressed in the end-effector frame into the camera frame.
| cVe | : Twist transformation. Here this transformation is equal to identity since camera frame and end-effector frame are at the same location. |
Definition at line 121 of file vpRobotCamera.cpp.
|
virtual |
Get the robot jacobian expressed in the end-effector frame. For that simple robot the Jacobian is the identity.
| eJe | : A 6 by 6 matrix representing the robot jacobian 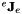 expressed in the end-effector frame. expressed in the end-effector frame. |
Implements vpRobot.
Definition at line 135 of file vpRobotCamera.cpp.
References vpRobot::eJe.
|
inherited |
Get the maximal rotation velocity that can be sent to the robot during a velocity control.
Definition at line 228 of file vpRobot.cpp.
Referenced by vpSimulatorAfma6::computeArticularVelocity(), vpSimulatorViper850::computeArticularVelocity(), vpSimulatorAfma6::findHighestPositioningSpeed(), vpSimulatorViper850::findHighestPositioningSpeed(), vpSimulatorAfma6::setPosition(), setVelocity(), vpSimulatorCamera::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneer::setVelocity(), vpRobotPioneer::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneerPan::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorAfma6::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorViper850::setVelocity(), vpRobotAfma4::setVelocity(), vpRobotAfma6::setVelocity(), vpRobotViper650::setVelocity(), and vpRobotViper850::setVelocity().
|
inherited |
Get the maximal translation velocity that can be sent to the robot during a velocity control.
Definition at line 203 of file vpRobot.cpp.
Referenced by vpSimulatorAfma6::setPosition(), setVelocity(), vpSimulatorCamera::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneer::setVelocity(), vpRobotPioneer::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneerPan::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorAfma6::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorViper850::setVelocity(), vpRobotAfma4::setVelocity(), vpRobotAfma6::setVelocity(), vpRobotViper650::setVelocity(), and vpRobotViper850::setVelocity().
| void vpRobotCamera::getPosition | ( | vpHomogeneousMatrix & | cMw | ) | const |
Get the robot position as the transformation from camera frame to world frame.
Definition at line 215 of file vpRobotCamera.cpp.
References cMw_.
|
virtual |
Get the robot position (frame has to be specified).
Implements vpRobot.
Definition at line 240 of file vpRobotCamera.cpp.
References vpRobot::ARTICULAR_FRAME, vpRxyzVector::buildFrom(), vpRobot::CAMERA_FRAME, cMw_, vpHomogeneousMatrix::extract(), vpRobot::MIXT_FRAME, vpRobot::REFERENCE_FRAME, and vpColVector::resize().
|
inherited |
Return the current robot position in the specified frame.
Definition at line 171 of file vpRobot.cpp.
|
inlineprotectedinherited |
Definition at line 159 of file vpRobot.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorAfma6::computeArticularVelocity(), and vpSimulatorViper850::computeArticularVelocity().
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Definition at line 139 of file vpRobot.h.
Referenced by vpRobotBiclops::getPosition(), vpRobotBiclops::getVelocity(), setPosition(), vpSimulatorCamera::setPosition(), vpRobotPtu46::setPosition(), vpRobotBiclops::setPosition(), vpSimulatorAfma6::setPosition(), vpSimulatorViper850::setPosition(), vpRobotAfma4::setPosition(), vpRobotAfma6::setPosition(), vpRobotViper650::setPosition(), vpRobotViper850::setPosition(), vpRobotPtu46::setRobotState(), vpRobotBiclops::setRobotState(), vpSimulatorAfma6::setRobotState(), vpSimulatorViper850::setRobotState(), vpRobotAfma4::setRobotState(), vpRobotAfma6::setRobotState(), vpRobotViper650::setRobotState(), vpRobotViper850::setRobotState(), setVelocity(), vpSimulatorCamera::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneer::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneerPan::setVelocity(), vpRobotPtu46::setVelocity(), vpRobotBiclops::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorAfma6::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorViper850::setVelocity(), vpRobotAfma4::setVelocity(), vpRobotAfma6::setVelocity(), vpRobotViper650::setVelocity(), vpRobotViper850::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorAfma6::stopMotion(), vpSimulatorViper850::stopMotion(), vpRobotViper650::stopMotion(), and vpRobotViper850::stopMotion().
|
inlineinherited |
Return the sampling time.
Definition at line 83 of file vpRobotSimulator.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorAfma6::updateArticularPosition(), and vpSimulatorViper850::updateArticularPosition().
|
staticinherited |
Saturate velocities.
| v_in | : Vector of input velocities to saturate. Translation velocities should be expressed in m/s while rotation velocities in rad/s. |
| v_max | : Vector of maximal allowed velocities. Maximal translation velocities should be expressed in m/s while maximal rotation velocities in rad/s. |
| verbose | : Print a message indicating which axis causes the saturation. |
| vpRobotException::dimensionError | : If the input vectors have different dimensions. |
The code below shows how to use this static method in order to saturate a velocity skew vector.
Definition at line 116 of file vpRobot.cpp.
References vpException::dimensionError, and vpColVector::size().
Referenced by setVelocity(), vpSimulatorCamera::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneer::setVelocity(), vpRobotPioneer::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneerPan::setVelocity(), vpRobotAfma4::setVelocity(), vpRobotAfma6::setVelocity(), vpRobotViper650::setVelocity(), and vpRobotViper850::setVelocity().
|
inherited |
Set the maximal rotation velocity that can be sent to the robot during a velocity control.
| w_max | : Maximum rotation velocity expressed in rad/s. |
Definition at line 215 of file vpRobot.cpp.
Referenced by vpSimulatorAfma6::setPosition().
|
inherited |
Set the maximal translation velocity that can be sent to the robot during a velocity control.
| v_max | : Maximum translation velocity expressed in m/s. |
Definition at line 191 of file vpRobot.cpp.
Referenced by vpSimulatorAfma6::setPosition().
| void vpRobotCamera::setPosition | ( | const vpHomogeneousMatrix & | cMw | ) |
Set the robot position as the transformation from camera frame to world frame.
Definition at line 274 of file vpRobotCamera.cpp.
References cMw_, vpRobot::getRobotState(), vpRobot::setRobotState(), and vpRobot::STATE_POSITION_CONTROL.
|
protectedinherited |
Definition at line 161 of file vpRobot.cpp.
Referenced by vpSimulatorAfma6::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpSimulatorCamera::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneer::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneerPan::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorAfma6::setVelocity(), and vpSimulatorViper850::setVelocity().
|
virtualinherited |
Reimplemented in vpRobotViper850, vpRobotViper650, vpRobotAfma6, vpRobotAfma4, vpSimulatorViper850, vpSimulatorAfma6, vpRobotBiclops, and vpRobotPtu46.
Definition at line 154 of file vpRobot.cpp.
Referenced by setPosition(), vpSimulatorCamera::setPosition(), vpRobotPtu46::setRobotState(), vpRobotBiclops::setRobotState(), vpSimulatorAfma6::setRobotState(), vpSimulatorViper850::setRobotState(), vpRobotAfma4::setRobotState(), vpRobotAfma6::setRobotState(), vpRobotViper650::setRobotState(), vpRobotViper850::setRobotState(), setVelocity(), vpSimulatorCamera::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneer::setVelocity(), and vpSimulatorPioneerPan::setVelocity().
|
inlinevirtualinherited |
Set the sampling time.
| delta_t | : Sampling time in second used to compute the robot displacement from the velocity applied to the robot during this time. |
Reimplemented in vpRobotWireFrameSimulator.
Definition at line 95 of file vpRobotSimulator.h.
Referenced by vpRobotSimulator::vpRobotSimulator().
|
virtual |
Send to the controller a velocity.
| frame | : Control frame type. Only articular (vpRobot::ARTICULAR_FRAME) and camera frame (vpRobot::CAMERA_FRAME) are implemented. |
| v | : Velocity to apply to the robot. |
![$ {\bf v} = [{\bf t}, {\bf \theta u }]^t $](form_492.png) where
where 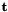 is a translation vector and
is a translation vector and 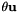 is a rotation vector (see vpThetaUVector):
is a rotation vector (see vpThetaUVector): ![$ {\bf v} = [t_x, t_y, t_z, {\theta u}_x, {\theta u}_y, {\theta u}_z] $](form_320.png) (see vpTranslationVector and vpThetaUVector).
(see vpTranslationVector and vpThetaUVector).![$ \dot{{\bf q}} = [{\bf t}, {\bf \theta u}]^t $](form_493.png) where
where 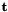 is a translation vector and
is a translation vector and 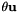 is a rotation vector (see vpThetaUVector):
is a rotation vector (see vpThetaUVector): ![$ \dot{{\bf q}} = [t_x, t_y, t_z, {\theta u}_x, {\theta u}_y, {\theta u}_z] $](form_494.png) (see vpTranslationVector and vpThetaUVector). The robot jacobian
(see vpTranslationVector and vpThetaUVector). The robot jacobian 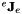 expressed in the end-effector frame is here set to identity.
expressed in the end-effector frame is here set to identity.We use the exponential map (vpExponentialMap) to update the camera location. Sampling time can be set using setSamplingTime().
Implements vpRobot.
Definition at line 169 of file vpRobotCamera.cpp.
References vpRobot::ARTICULAR_FRAME, vpRobot::CAMERA_FRAME, cMw_, vpRobotSimulator::delta_t_, vpExponentialMap::direct(), vpRobot::getMaxRotationVelocity(), vpRobot::getMaxTranslationVelocity(), vpRobot::getRobotState(), vpHomogeneousMatrix::inverse(), vpRobot::MIXT_FRAME, vpRobot::REFERENCE_FRAME, vpRobot::saturateVelocities(), vpRobot::setRobotState(), vpRobot::STATE_VELOCITY_CONTROL, vpERROR_TRACE, and vpRobotException::wrongStateError.
|
inlineinherited |
Definition at line 155 of file vpRobot.h.
Referenced by vpRobotAfma4::vpRobotAfma4(), vpRobotAfma6::vpRobotAfma6(), vpRobotViper650::vpRobotViper650(), and vpRobotViper850::vpRobotViper850().
|
protected |
Definition at line 113 of file vpRobotCamera.h.
Referenced by getPosition(), setPosition(), and setVelocity().
|
protectedinherited |
Definition at line 68 of file vpRobotSimulator.h.
Referenced by setVelocity(), vpSimulatorCamera::setVelocity(), vpSimulatorPioneer::setVelocity(), and vpSimulatorPioneerPan::setVelocity().
|
protectedinherited |
robot Jacobian expressed in the end-effector frame
Definition at line 103 of file vpRobot.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorAfma6::computeArticularVelocity(), vpSimulatorViper850::computeArticularVelocity(), get_eJe(), vpSimulatorCamera::get_eJe(), vpSimulatorAfma6::getVelocity(), vpSimulatorViper850::getVelocity(), vpSimulatorAfma6::setPosition(), and vpRobotAfma4::setVelocity().
|
protectedinherited |
|
protectedinherited |
robot Jacobian expressed in the robot reference frame available
Definition at line 107 of file vpRobot.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorAfma6::computeArticularVelocity(), vpSimulatorViper850::computeArticularVelocity(), vpSimulatorAfma6::getVelocity(), and vpSimulatorViper850::getVelocity().
|
protectedinherited |
|
staticprotectedinherited |
|
staticprotectedinherited |
|
protectedinherited |
|
protectedinherited |
Definition at line 115 of file vpRobot.h.
Referenced by vpRobotAfma4::init(), vpRobotAfma6::init(), vpRobotViper650::init(), vpRobotViper850::init(), vpRobot::vpRobot(), vpRobotAfma4::vpRobotAfma4(), vpRobotAfma6::vpRobotAfma6(), vpRobotViper650::vpRobotViper650(), and vpRobotViper850::vpRobotViper850().