 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.2.0 under development (2019-01-22)
|
 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.2.0 under development (2019-01-22)
|
#include <visp3/core/vpQuadProg.h>
Public Member Functions | |
Instanciated solvers | |
| bool | solveQPe (const vpMatrix &Q, const vpColVector &r, vpColVector &x, const double &tol=1e-6) const |
| bool | solveQPi (const vpMatrix &Q, const vpColVector &r, const vpMatrix &C, const vpColVector &d, vpColVector &x, const bool use_equality=false, const double &tol=1e-6) |
| bool | solveQP (const vpMatrix &Q, const vpColVector &r, vpMatrix A, vpColVector b, const vpMatrix &C, const vpColVector &d, vpColVector &x, const double &tol=1e-6) |
Managing sequential calls to solvers | |
| bool | setEqualityConstraint (const vpMatrix &A, const vpColVector &b, const double &tol=1e-6) |
| void | resetActiveSet () |
Static Public Member Functions | |
| static void | fromCanonicalCost (const vpMatrix &H, const vpColVector &c, vpMatrix &Q, vpColVector &r, const double &tol=1e-6) |
| static bool | solveQPe (const vpMatrix &Q, const vpColVector &r, vpMatrix A, vpColVector b, vpColVector &x, const double &tol=1e-6) |
Static Protected Member Functions | |
| static bool | solveByProjection (const vpMatrix &Q, const vpColVector &r, vpMatrix &A, vpColVector &b, vpColVector &x, const double &tol=1e-6) |
| static unsigned int | checkDimensions (const vpMatrix &Q, const vpColVector &r, const vpMatrix *A, const vpColVector *b, const vpMatrix *C, const vpColVector *d, const std::string fct) |
Protected Attributes | |
| std::vector< unsigned int > | active |
| std::vector< unsigned int > | inactive |
| vpColVector | x1 |
| vpMatrix | Z |
This class provides a solver for Quadratic Programs.
The cost function is written under the form 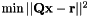 .
.
If a cost function is written under the canonical form 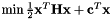 then fromCanonicalCost() can be used to retrieve Q and r from H and c.
then fromCanonicalCost() can be used to retrieve Q and r from H and c.
Equality constraints are solved through projection into the kernel.
Inequality constraints are solved with active sets.
In order to be used sequentially, the decomposition of the equality constraint may be stored. The last active set is always stored and used to warm start the next call.
Definition at line 73 of file vpQuadProg.h.
|
inlinestaticprotected |
Performs a dimension check of passed QP matrices and vectors.
If any inconsistency is detected, displays a summary and throws an exception.
| Q | : cost matrix (dimension c x n) |
| r | : cost vector (dimension c) |
| A | : pointer to the equality matrix (if any, dimension m x n) |
| b | : pointer to the equality vector (if any, dimension m) |
| C | : pointer to the inequality matrix (if any, dimension p x n) |
| d | : pointer to the inequality vector (if any, dimension p) |
| fct | : name of the solver that called this function |
Definition at line 148 of file vpQuadProg.h.
References vpException::dimensionError, vpArray2D< Type >::getCols(), and vpArray2D< Type >::getRows().
Referenced by solveQP(), solveQPe(), and solveQPi().
|
static |
Changes a canonical quadratic cost 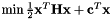 to the formulation used by this class
to the formulation used by this class 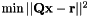 .
.
Computes 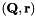 such that
such that 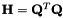 and
and 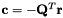 .
.
| H | : canonical symmetric positive cost matrix (dimension n x n) |
| c | : canonical cost vector (dimension n) |
| Q | : custom cost matrix (dimension rank(H) x n) |
| r | : custom cost vector (dimension rank(H)) |
| tol | : tolerance to test ranks |
Here is an example:
![$\begin{array}{lll} \mathbf{x} = & \arg\min & 2x_1^2 + x_2^2 + x_1x_2 + x_1 + x_2\\ & \text{s.t.}& x_1 + x_2 = 1 \end{array} \Leftrightarrow \begin{array}{lll} \mathbf{x} = & \arg\min & \frac{1}{2}\mathbf{x}^T\left[\begin{array}{cc}4 & 1 \\ 1 & 2\end{array}\right]\mathbf{x} + [1~1]\mathbf{x}\\ & \text{s.t.}& [1~1]\mathbf{x} = 1 \end{array} $](form_1350.png)
Definition at line 98 of file vpQuadProg.cpp.
References vpMatrix::diag(), vpException::dimensionError, vpMatrix::eigenValues(), vpColVector::extract(), vpException::functionNotImplementedError, vpArray2D< Type >::getCols(), vpArray2D< Type >::getRows(), vpMatrixException::matrixError, vpMatrix::pseudoInverse(), vpMatrix::t(), and vpMatrix::transpose().
|
inline |
Resets the active set that was found by a previous call to solveQP() or solveQPi(), if any.
Definition at line 100 of file vpQuadProg.h.
| bool vpQuadProg::setEqualityConstraint | ( | const vpMatrix & | A, |
| const vpColVector & | b, | ||
| const double & | tol = 1e-6 |
||
| ) |
Saves internally the column reduction of the passed equality constraint:
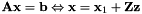
| A | : equality matrix (dimension m x n) |
| b | : equality vector (dimension m) |
| tol | : tolerance to test the ranks |
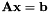 has a solution.
has a solution.Definition at line 155 of file vpQuadProg.cpp.
References vpLinProg::colReduction(), vpArray2D< Type >::getRows(), x1, and Z.
|
staticprotected |
Solves a Quadratic Program under equality constraints.
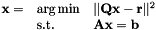
| Q | : cost matrix (dimension c x n) |
| r | : cost vector (dimension c) |
| A | : equality matrix (dimension m x n) |
| b | : equality vector (dimension m) |
| x | : solution (dimension n) |
| tol | : tolerance to test the ranks |
This function is for internal use, no dimension check is performed and A and b may be modified.
Definition at line 184 of file vpQuadProg.cpp.
References vpLinProg::colReduction(), vpArray2D< Type >::getCols(), vpArray2D< Type >::getRows(), and vpMatrix::solveBySVD().
Referenced by solveQPe(), and solveQPi().
| bool vpQuadProg::solveQP | ( | const vpMatrix & | Q, |
| const vpColVector & | r, | ||
| vpMatrix | A, | ||
| vpColVector | b, | ||
| const vpMatrix & | C, | ||
| const vpColVector & | d, | ||
| vpColVector & | x, | ||
| const double & | tol = 1e-6 |
||
| ) |
Solves a Quadratic Program under equality and inequality constraints.
If the equality constraints 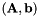 are the same between two calls, it is more efficient to use setEqualityConstraint() and solveQPi().
are the same between two calls, it is more efficient to use setEqualityConstraint() and solveQPi().

| Q | : cost matrix (dimension c x n) |
| r | : cost vector (dimension c) |
| A | : equality matrix (dimension m x n) |
| b | : equality vector (dimension m) |
| C | : inequality matrix (dimension p x n) |
| d | : inequality vector (dimension p) |
| x | : solution (dimension n) |
| tol | : tolerance to test the ranks |
Here is an example:

Definition at line 389 of file vpQuadProg.cpp.
References vpLinProg::allLesser(), checkDimensions(), vpLinProg::colReduction(), vpArray2D< Type >::getCols(), vpArray2D< Type >::getRows(), and solveQPi().
| bool vpQuadProg::solveQPe | ( | const vpMatrix & | Q, |
| const vpColVector & | r, | ||
| vpColVector & | x, | ||
| const double & | tol = 1e-6 |
||
| ) | const |
Solves a Quadratic Program under previously stored equality constraints (setEqualityConstraint())
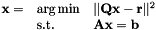
| Q | : cost matrix (dimension c x n) |
| r | : cost vector (dimension c) |
| x | : solution (dimension n) |
| tol | : Tolerance. |
Here is an example where the two following QPs are solved:
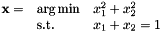
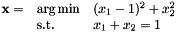
Definition at line 255 of file vpQuadProg.cpp.
References vpException::dimensionError, vpArray2D< Type >::getCols(), vpArray2D< Type >::getRows(), vpMatrix::solveBySVD(), x1, and Z.
|
static |
Solves a Quadratic Program under equality constraints.
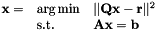
If the equality constraints 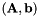 are the same between two calls, it is more efficient to use setEqualityConstraint() and solveQPe().
are the same between two calls, it is more efficient to use setEqualityConstraint() and solveQPe().
| Q | : cost matrix (dimension c x n) |
| r | : cost vector (dimension c) |
| A | : equality matrix (dimension m x n) |
| b | : equality vector (dimension m) |
| x | : solution (dimension n) |
| tol | : tolerance to test the ranks |
Here is an example:
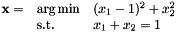
Definition at line 325 of file vpQuadProg.cpp.
References checkDimensions(), and solveByProjection().
| bool vpQuadProg::solveQPi | ( | const vpMatrix & | Q, |
| const vpColVector & | r, | ||
| const vpMatrix & | C, | ||
| const vpColVector & | d, | ||
| vpColVector & | x, | ||
| const bool | use_equality = false, |
||
| const double & | tol = 1e-6 |
||
| ) |
Solves a Quadratic Program under inequality constraints
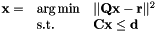
| Q | : cost matrix (dimension c x n) |
| r | : cost vector (dimension c) |
| C | : inequality matrix (dimension p x n) |
| d | : inequality vector (dimension p) |
| x | : solution (dimension n) |
| use_equality | : if a previously saved equality constraint (setEqualityConstraint()) should be considered |
| tol | : tolerance to test the ranks |
Here is an example:

Definition at line 465 of file vpQuadProg.cpp.
References active, vpLinProg::allGreater(), vpLinProg::allLesser(), vpLinProg::allZero(), checkDimensions(), vpColVector::clear(), vpColVector::extract(), vpArray2D< Type >::getCols(), vpMatrix::getRow(), vpArray2D< Type >::getRows(), inactive, vpMatrix::pseudoInverse(), vpArray2D< Type >::resize(), vpColVector::resize(), vpLinProg::simplex(), vpArray2D< Type >::size(), solveByProjection(), vpMatrix::transpose(), x1, and Z.
Referenced by solveQP().
|
protected |
Active set from the last call to solveQP() or solveQPi(). Used for warm starting the next call.
Definition at line 115 of file vpQuadProg.h.
Referenced by solveQPi().
|
protected |
Inactive set from the last call to solveQP() or solveQPi(). Used for warm starting the next call.
Definition at line 119 of file vpQuadProg.h.
Referenced by solveQPi().
|
protected |
Stored particular solution from the last call to setEqualityConstraint().
Definition at line 123 of file vpQuadProg.h.
Referenced by setEqualityConstraint(), solveQPe(), and solveQPi().
|
protected |
Stored projection to the kernel from the last call to setEqualityConstraint().
Definition at line 127 of file vpQuadProg.h.
Referenced by setEqualityConstraint(), solveQPe(), and solveQPi().