 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.0.0
|
 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.0.0
|
#include <visp3/io/vpVideoReader.h>
 Inheritance diagram for vpVideoReader:
Inheritance diagram for vpVideoReader:Public Member Functions | |
| vpVideoReader () | |
| ~vpVideoReader () | |
| void | acquire (vpImage< vpRGBa > &I) |
| void | acquire (vpImage< unsigned char > &I) |
| void | close () |
| bool | end () |
| bool | getFrame (vpImage< vpRGBa > &I, long frame) |
| bool | getFrame (vpImage< unsigned char > &I, long frame) |
| double | getFramerate () |
| long | getFrameIndex () const |
| long | getFirstFrameIndex () const |
| long | getLastFrameIndex () const |
| void | open (vpImage< vpRGBa > &I) |
| void | open (vpImage< unsigned char > &I) |
| void | resetFrameCounter () |
| void | setFileName (const char *filename) |
| void | setFileName (const std::string &filename) |
| void | setFirstFrameIndex (const long first_frame) |
| void | setLastFrameIndex (const long last_frame) |
| unsigned int | getHeight () const |
| unsigned int | getWidth () const |
Public Attributes | |
| bool | init |
Protected Attributes | |
| unsigned int | height |
| unsigned int | width |
Class that enables to manipulate easily a video file or a sequence of images. As it inherits from the vpFrameGrabber Class, it can be used like an other frame grabber class.
The following example available in tutorial-video-reader.cpp shows how this class is really easy to use. It enables to read a video file named video.mpeg.
As shown in the next example, this class allows also to access to a specific frame. But be careful, for video files, the getFrame() method is not precise and returns the nearest intra key frame from the expected frame. You can use the getFrame() method to position the reader in the video and then use the acquire() method to get the following frames one by one.
The other following example explains how to use the class to read a sequence of images. The images are stored in the folder "./image" and are named "image0000.jpeg", "image0001.jpeg", "image0002.jpeg", ... As explained in setFirstFrameIndex() and setLastFrameIndex() it is also possible to set the first and last image numbers to read a portion of the sequence. If these two functions are not used, first and last image numbers are set automatically to match the first and image images of the sequence.
Note that it is also possible to access to a specific frame using getFrame().
Definition at line 159 of file vpVideoReader.h.
| vpVideoReader::vpVideoReader | ( | ) |
Basic constructor.
Definition at line 54 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
| vpVideoReader::~vpVideoReader | ( | ) |
Basic destructor.
Definition at line 69 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
Grabs the current (k) image in the stack of frames and increments the frame counter in order to grab the next image (k+1) during the next use of the method. If open() was not called previously, this method opens the video reader.
This method enables to use the class as frame grabber.
| I | : The image where the frame is stored. |
Implements vpFrameGrabber.
Definition at line 268 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
References vpDiskGrabber::acquire(), vpFFMPEG::acquire(), vpImageConvert::convert(), open(), and setLastFrameIndex().
|
virtual |
Grabs the kth image in the stack of frames and increments the frame counter in order to grab the next image (k+1) during the next use of the method.
This method enables to use the class as frame grabber.
| I | : The image where the frame is stored. |
Implements vpFrameGrabber.
Definition at line 312 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
References vpDiskGrabber::acquire(), vpFFMPEG::acquire(), vpImageConvert::convert(), open(), and setLastFrameIndex().
|
inlinevirtual |
This virtual function is used to de-allocate the memory used by a specific frame grabber
Implements vpFrameGrabber.
Definition at line 242 of file vpVideoReader.h.
|
inline |
Definition at line 247 of file vpVideoReader.h.
|
inline |
Gets the first frame index.
Definition at line 270 of file vpVideoReader.h.
Gets the 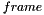 th frame and stores it in the image
th frame and stores it in the image 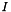 .
.
| I | : The vpImage used to stored the frame. |
| frame_index | : The index of the frame which has to be read. |
Definition at line 360 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
References vpDiskGrabber::acquire(), vpImageConvert::convert(), vpFFMPEG::getFrame(), setLastFrameIndex(), and vpERROR_TRACE.
Referenced by open().
| bool vpVideoReader::getFrame | ( | vpImage< unsigned char > & | I, |
| long | frame_index | ||
| ) |
Gets the 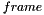 th frame and stores it in the image
th frame and stores it in the image 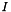 .
.
| I | : The vpImage used to stored the frame. |
| frame_index | : The index of the frame which has to be read. |
Definition at line 438 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
References vpDiskGrabber::acquire(), vpImageConvert::convert(), vpFFMPEG::getFrame(), setLastFrameIndex(), and vpERROR_TRACE.
|
inline |
Get the frame index of the next image. This index is updated at each call of the acquire method. It can be used to detect the end of a file (comparison with getLastFrameIndex()).
Definition at line 263 of file vpVideoReader.h.
| double vpVideoReader::getFramerate | ( | ) |
Return the framerate in Hz used to encode the video stream.
If the video is a sequence of images, return -1.
Definition at line 720 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
References vpFFMPEG::getFramerate(), and vpERROR_TRACE.
|
inlineinherited |
Return the number of rows in the image.
Definition at line 113 of file vpFrameGrabber.h.
|
inline |
Gets the last frame index.
Definition at line 276 of file vpVideoReader.h.
|
inlineinherited |
Return the number of columns in the image.
Definition at line 115 of file vpFrameGrabber.h.
Sets all the parameters needed to read the video or the image sequence.
Grab the first frame and stores it in the image 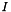 .
.
| I | : The image where the frame is stored. |
Implements vpFrameGrabber.
Definition at line 138 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
References vpFFMPEG::COLORED, vpException::fatalError, getFrame(), vpImage< Type >::getHeight(), vpImage< Type >::getWidth(), vpFrameGrabber::height, vpFFMPEG::initStream(), vpException::ioError, vpImageException::noFileNameError, vpFFMPEG::openStream(), vpDiskGrabber::setGenericName(), vpDiskGrabber::setImageNumber(), vpERROR_TRACE, and vpFrameGrabber::width.
Referenced by acquire().
|
virtual |
Sets all the parameters needed to read the video or the image sequence.
Grab the first frame and stores it in the image 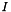 .
.
| I | : The image where the frame is stored. |
Implements vpFrameGrabber.
Definition at line 202 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
References vpException::fatalError, getFrame(), vpImage< Type >::getHeight(), vpImage< Type >::getWidth(), vpFFMPEG::GRAY_SCALED, vpFrameGrabber::height, vpFFMPEG::initStream(), vpException::ioError, vpImageException::noFileNameError, vpFFMPEG::openStream(), vpDiskGrabber::setGenericName(), vpDiskGrabber::setImageNumber(), vpERROR_TRACE, and vpFrameGrabber::width.
|
inline |
Reset the frame counter and sets it to the first image index.
By default the first frame index is set to 0.
This method is useful if you use the class like a frame grabber (ie with theacquire method).
Definition at line 287 of file vpVideoReader.h.
| void vpVideoReader::setFileName | ( | const char * | filename | ) |
It enables to set the path and the name of the file(s) which as/have to be read.
If you want to read a video file, 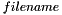 corresponds to the path to the file (example : /local/video.mpeg).
corresponds to the path to the file (example : /local/video.mpeg).
If you want to read a sequence of images, 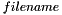 corresponds to the path followed by the image name template. For exemple, if you want to read different images named image0001.jpeg, image0002.jpg, ... and located in the folder /local/image,
corresponds to the path followed by the image name template. For exemple, if you want to read different images named image0001.jpeg, image0002.jpg, ... and located in the folder /local/image, 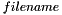 will be "/local/image/image%04d.jpg".
will be "/local/image/image%04d.jpg".
| filename | : Path to a video file or file name template of a image sequence. |
Definition at line 93 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
References vpException::badValue, vpException::memoryAllocationError, vpImageException::noFileNameError, and vpERROR_TRACE.
Referenced by setFileName().
| void vpVideoReader::setFileName | ( | const std::string & | filename | ) |
It enables to set the path and the name of the file(s) which as/have to be read.
If you want to read a video file, 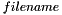 corresponds to the path to the file (example : /local/video.mpeg).
corresponds to the path to the file (example : /local/video.mpeg).
If you want to read a sequence of images, 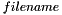 corresponds to the path followed by the image name template. For exemple, if you want to read different images named image0001.jpeg, image0002.jpg, ... and located in the folder /local/image,
corresponds to the path followed by the image name template. For exemple, if you want to read different images named image0001.jpeg, image0002.jpg, ... and located in the folder /local/image, 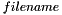 will be "/local/image/image%04d.jpg".
will be "/local/image/image%04d.jpg".
| filename | : Path to a video file or file name template of a image sequence. |
Definition at line 126 of file vpVideoReader.cpp.
References setFileName().
|
inline |
Enables to set the first frame index if you want to use the class like a grabber (ie with the acquire method).
| first_frame | : The first frame index. |
Definition at line 298 of file vpVideoReader.h.
|
inline |
Enables to set the last frame index.
| last_frame | : The last frame index. |
Definition at line 309 of file vpVideoReader.h.
Referenced by acquire(), and getFrame().
|
protectedinherited |
Number of rows in the image.
Definition at line 107 of file vpFrameGrabber.h.
Referenced by vpDiskGrabber::acquire(), vpV4l2Grabber::acquire(), vp1394TwoGrabber::acquire(), vp1394TwoGrabber::dequeue(), vp1394TwoGrabber::getHeight(), vpDiskGrabber::open(), vpV4l2Grabber::open(), vp1394CMUGrabber::open(), open(), vp1394TwoGrabber::setFormat7ROI(), vp1394CMUGrabber::setVideoMode(), vp1394TwoGrabber::setVideoMode(), vp1394CMUGrabber::vp1394CMUGrabber(), and vp1394TwoGrabber::vp1394TwoGrabber().
|
inherited |
Set to true if the frame grabber has been initialized.
Definition at line 105 of file vpFrameGrabber.h.
Referenced by vpV4l2Grabber::acquire(), vp1394CMUGrabber::close(), vp1394TwoGrabber::close(), vpDiskGrabber::open(), vpV4l2Grabber::open(), vp1394TwoGrabber::resetBus(), vp1394CMUGrabber::vp1394CMUGrabber(), vp1394TwoGrabber::vp1394TwoGrabber(), vpDiskGrabber::vpDiskGrabber(), and vpV4l2Grabber::vpV4l2Grabber().
|
protectedinherited |
Number of columns in the image.
Definition at line 108 of file vpFrameGrabber.h.
Referenced by vpDiskGrabber::acquire(), vpV4l2Grabber::acquire(), vp1394TwoGrabber::acquire(), vp1394TwoGrabber::dequeue(), vp1394TwoGrabber::getWidth(), vpDiskGrabber::open(), vpV4l2Grabber::open(), vp1394CMUGrabber::open(), open(), vp1394TwoGrabber::setFormat7ROI(), vp1394CMUGrabber::setVideoMode(), vp1394TwoGrabber::setVideoMode(), vp1394CMUGrabber::vp1394CMUGrabber(), and vp1394TwoGrabber::vp1394TwoGrabber().