Introduction
Statistical Process Control (SPC) is defined as the use of statistical methods to monitor if a signal is "in control".
In this tutorial, we will use a Statistical Process Control method to monitor if a random signal following a normal distribution is "in control".
Available methods
The different methods available in ViSP aim at detecting if the mean of a signal is changing, either due to an abrupt jump or due to a slow drift.
The different methods that are available are the following:
We refer the reader to the documentation of each class to have more detailed information on each method.
Explanations about the tutorial
How to run the tutorial
To see the different options of the tutorial, please run the following commands:
$ cd $VISP_WS/
visp-build/tutorial/mean-drift
$ ./tutorial-meandrift -h
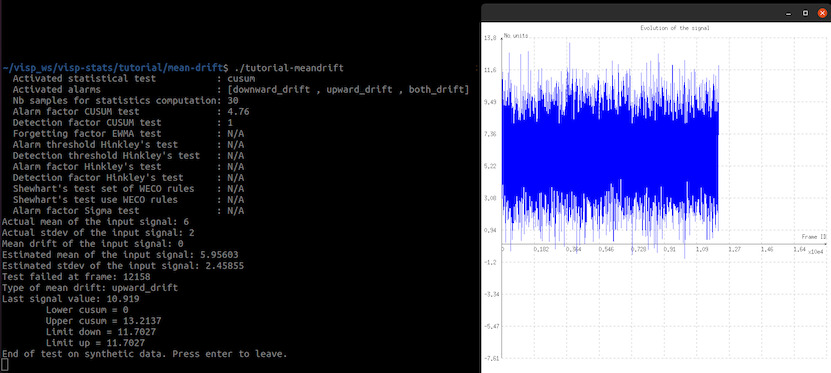
If you run the program without argument, you should see something similar to the following image:
A Gaussian signal of mean equal to 6 and of standard deviation equal to 2 is generated, without any mean drift. The program tells you which method has been chosen in the console, and which are its parameters. A monitoring loop stops once an alarm is raised. When the alarm is raised, some information about the alarm and the test signal(s) + limits of the SPC method are given. Press Return to leave the program.
Detailed explanations about the SPC tutorial
For this tutorial, we use the main program tutorial-meandrift.cpp .
It uses the following enumeration to let the user choose which SPC method to use to monitor the signal:
typedef enum TypeTest
{
HINLKEY_TYPE_TEST = 0,
EWMA_TYPE_TEST = 1,
MEAN_ADJUSTED_CUSUM_TYPE_TEST = 2,
SHEWHART_TYPE_TEST = 3,
SIGMA_TYPE_TEST = 4,
COUNT_TYPE_TEST = 5,
UNKOWN_TYPE_TEST = COUNT_TYPE_TEST
}TypeTest;
The program arguments are parsed and fill the following structure that stores the SPC methods parameters:
typedef struct ParametersForAlgo
{
unsigned int m_test_nbsamples;
unsigned int m_test_nbactivatedalarms;
float m_cusum_h;
float m_cusum_k;
float m_ewma_alpha;
float m_hinkley_alpha;
float m_hinkley_delta;
bool m_hinkley_computealphadelta;
float m_hinkley_h;
float m_hinkley_k;
bool m_shewhart_useWECO;
std::vector<bool> m_shewhart_rules;
float m_sigma_h;
ParametersForAlgo()
: m_test_nbsamples(30)
, m_cusum_h(4.76f)
, m_cusum_k(1.f)
, m_ewma_alpha(0.1f)
, m_hinkley_alpha(4.76f)
, m_hinkley_delta(1.f)
, m_hinkley_computealphadelta(false)
, m_hinkley_h(4.76f)
, m_hinkley_k(1.f)
, m_shewhart_useWECO(false)
, m_sigma_h(3.f)
{
m_test_nbactivatedalarms = meanDriftArrayToNbActivated(m_test_activatedalarms);
}
}ParametersForAlgo;
static const std::vector< bool > CONST_ALL_WECO_ACTIVATED
It is possible to choose to monitor only upward mean drifts, only downward mean drifts or both. To do so, use the --alarms option with the name of the alarm(s) you want to monitor.
First, the plot that will show the data is created in the following section of code:
plotter.initGraph(0, 1);
plotter.setTitle(0, "Evolution of the signal");
plotter.setUnitX(0, "Frame ID");
plotter.setUnitY(0, "No units");
This class enables real time drawing of 2D or 3D graphics. An instance of the class open a window whi...
Then, the desired method is created in the following section of code, with the desired parameters:
unsigned int idFrame = 0;
switch (type) {
case TutorialMeanDrift::EWMA_TYPE_TEST:
break;
case TutorialMeanDrift::HINLKEY_TYPE_TEST:
p_test =
new vpStatisticalTestHinkley(parameters.m_hinkley_alpha, parameters.m_hinkley_delta, parameters.m_test_nbsamples);
break;
case TutorialMeanDrift::MEAN_ADJUSTED_CUSUM_TYPE_TEST:
break;
case TutorialMeanDrift::SHEWHART_TYPE_TEST:
p_test =
new vpStatisticalTestShewhart(parameters.m_shewhart_useWECO, parameters.m_shewhart_rules, parameters.m_test_nbsamples);
break;
case TutorialMeanDrift::SIGMA_TYPE_TEST:
break;
default:
break;
}
if ((type == TutorialMeanDrift::HINLKEY_TYPE_TEST) && parameters.m_hinkley_computealphadelta) {
delete p_test;
p_test =
new vpStatisticalTestHinkley(parameters.m_hinkley_h, parameters.m_hinkley_k,
true, parameters.m_test_nbsamples);
}
error that can be emitted by ViSP classes.
@ badValue
Used to indicate that a value is not in the allowed range.
Base class for methods detecting the drift of the mean of a process.
Class that permits to perform Exponentially Weighted Moving Average mean drft tests.
This class implements the Hinkley's cumulative sum test.
Class that permits to perform a mean adjusted Cumulative Sum test.
Class that permits a Shewhart's test.
Class that permits a simple test comparing the current value to the standard deviation of the signal.
Then, the method is filled with "in control" signals to initialize the expected mean and the standard deviation:
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < parameters.m_test_nbsamples; ++i) {
vpGaussRand rndGen(stdev, mean,
static_cast<long>(idFrame * dt));
signal = static_cast<float>(rndGen());
++idFrame;
}
Class for generating random number with normal probability density.
vpMeanDriftType testDownUpwardMeanDrift(const float &signal)
Test if a downward or an upward mean drift occurred according to the new value of the signal.
Then, the monitoring loop is run, where the signal is randomly generated with a potential mean drift (if desired). This random signal is then tested, and the loop is stopped if an alarm we want to monitor is raised:
float mean_eff = mean;
bool hasToRun = true;
while (hasToRun) {
vpGaussRand rndGen(stdev, mean_eff,
static_cast<long>(idFrame * dt));
signal = static_cast<float>(rndGen());
plotter.plot(0, 0, idFrame - parameters.m_test_nbsamples, signal);
hasToRun = false;
}
else {
mean_eff += mean_drift;
++idFrame;
}
}
vpMeanDriftType
Enum that indicates if a drift of the mean occurred.
Finally, some information about why the loop was stopped is displayed in the console:
std::cout << "Test failed at frame: " << idFrame - parameters.m_test_nbsamples << std::endl;
std::cout << "Last signal value: " << signal << std::endl;
if (type == TutorialMeanDrift::EWMA_TYPE_TEST) {
std::cout <<
"\tw(t) = " << p_testEwma->
getWt() << std::endl;
}
else if (type == TutorialMeanDrift::MEAN_ADJUSTED_CUSUM_TYPE_TEST) {
}
else if (type==TutorialMeanDrift::SHEWHART_TYPE_TEST) {
std::vector<float> signal = p_testShewhart->
getSignals();
size_t nbSignal = signal.size();
std::cout << "Signal history = [ ";
for (size_t i = 0; i < nbSignal; ++i) {
std::cout << signal[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << "]" << std::endl;
}
else if (type == TutorialMeanDrift::HINLKEY_TYPE_TEST) {
float Mk = p_hinkley->
getMk();
float Nk = p_hinkley->
getNk();
float Sk = p_hinkley->
getSk();
float Tk = p_hinkley->
getTk();
std::cout << "S+(t) = " << Tk - Nk <<std::endl;
std::cout << "S-(t) = " << Mk - Sk <<std::endl;
}
float limitDown = 0.f, limitUp = 0.f;
std::cout << "\tLimit down = " << limitDown << std::endl;
std::cout << "\tLimit up = " << limitUp << std::endl;
static std::string vpMeanDriftTypeToString(const vpMeanDriftType &type)
Cast a vpMeanDriftType into a string.
void getLimits(float &limitDown, float &limitUp) const
Get the upper and lower limits of the test signal.
float getWt() const
Get the current value of the test signal.
float getNk() const
Get the minimum of the test signal for upward mean drift .
float getTk() const
Get the test signal for upward mean drift..
float getSk() const
Get the test signal for downward mean drift.
float getMk() const
Get the maximum of the test signal for downward mean drift .
float getTestSignalMinus() const
Get the latest value of the test signal for downward jumps of the mean.
float getTestSignalPlus() const
Get the latest value of the test signal for upward jumps of the mean.
vpWecoRulesAlarm getAlarm() const
Get the alarm raised by the last test due to the WECO's rules.
std::vector< float > getSignals() const
Get the NB_DATA_SIGNAL last signal values, sorted from the latest [0] to the newest [NB_DATA_SIGNAL -...
static std::string vpWecoRulesAlarmToString(const vpWecoRulesAlarm &alarm)
The program stops once the Return key is pressed.