 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.5.1 under development (2022-10-02)
|
 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.5.1 under development (2022-10-02)
|
In this tutorial you will learn how to install ViSP from source on Windows 10 with MinGW-W64. These steps have been tested with CMake 3.19.0 and MinGW-W64 - GCC for Windows 64 & 32 bits.
mingw-w64-install.exe. It opens a window where you have to select some options. As in the next image, we recommend to select version 8.1.0 (the last version available when this tutorial was updated), architecture x86_64, posix threads that enables std::thread usage and exception seh (for Structured Exception Handling mechanism). 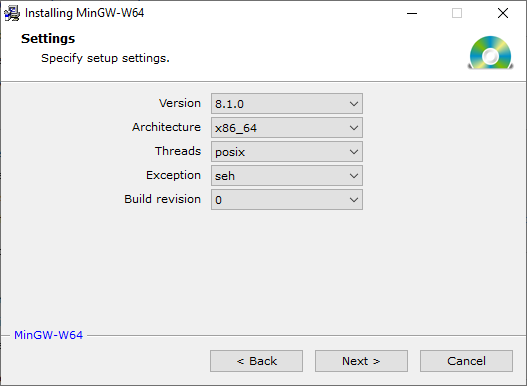
C:\Program Files\mingw-w64\x86_64-8.1.0-posix-seh-rt_v6-rev0 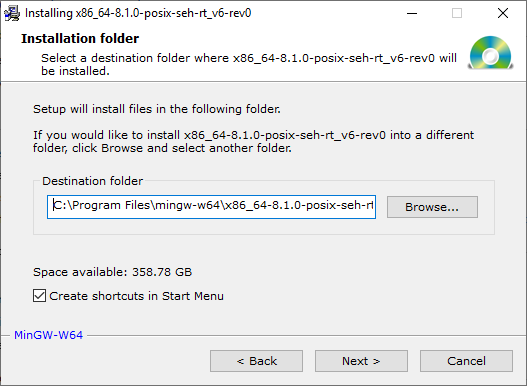
C:\Program Files\mingw-w64\x86_64-8.1.0-posix-seh-rt_v6-rev0\mingw64\bin folder to the Path variable. To this end open cmd Comand Prompt and do the following: C:\> setx Path "%Path%;C:\Program Files\mingw-w64\x86_64-8.1.0-posix-seh-rt_v6-rev0\mingw64\bin" C:\> exit
setx command is not able to handle a var that has more than 1024 characters (which could be the case of Path var), it may happen that the previous command is not working as expected. In that case, to modify Path environment variable do the following:C:\Program Files\mingw-w64\x86_64-8.1.0-posix-seh-rt_v6-rev0\mingw64\bincmd Command Prompt, and run: C:\> mingw32-make --version GNU Make 4.2.1 Built for x86_64-w64-mingw32 C:\> g++ --version g++ (x86_64-posix-seh-rev0, Built by MinGW-W64 project) 8.1.0
CMake could be download from http://www.cmake.org. Download the latest release for Windows win64-x64 platform (at the time this tutorial was written it was the file cmake-3.19.0-win64-x64.msi). To install just double click on the msi file.
Install Git for Windows from https://git-for-windows.github.io/. This installation allows then to use git in a cmd Command Prompt.
If not already done, create a workspace that will contain all ViSP source, build, data set and optional 3rd parties. This workspace is here set to C:\visp-ws folder, but it could be set to any other location.
To create the workspace, open a cmd Command Prompt (a fast way to launch this window is to press the Win + R keys on your keyboard. Then, type cmd or cmd.exe and press Enter or click/tap OK) and run the following to create a workspace environment var named VISP_WS:
C:\> setx VISP_WS "C:\visp-ws" C:\> exit
Open a new cmd Command Prompt and create the corresponding folder
C:\> mkdir %VISP_WS% C:\> exit
In this section, we give minimal instructions to build ViSP from source just to try ViSP without entering in Advanced ViSP installation.
cmd Command Prompt and get ViSP source code in the workspace C:\> cd %VISP_WS% C:\> git clone https://github.com/lagadic/visp.git
C:\> mkdir %VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw C:\> cd %VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw
C:\> cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles" %VISP_WS%\visp
C:\> cmake --build . --config Release --target install -j4
%VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw\install folderPath var to add %VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw\install\x64\mingw\bin corresponding to the path to ViSP libraries. To modify Path environment variable do the following:%VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw\install\x64\mingw\binVISP_DIR var to help CMake to find ViSP as a 3rd party C:\> setx VISP_DIR "%VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw\install" C:\> exit
To have a trial, just jump to Install ViSP data set before running some binaries that you just build or jump to Next tutorial. You can later come back to the Advanced ViSP installation.
ViSP is interfaced with several 3rd party libraries. The complete list is provided here. We recommend to install Eigen3 3rd party and OpenCV 3rd party in the workspace.
Even if Eigen3 is designed as a template we recommend to install the library with MinGW.
1. Get Eigen3
eigen-3.3.9.zip archive corresponding to Eigen 3.3.9.%VISP_WS%.%VISP_WS%\eigen-3.3.92. Build and install Eigen3 from source
C:\> mkdir %VISP_WS%\eigen-3.3.9\build-mingw C:\> cd %VISP_WS%\eigen-3.3.\build-mingw
%VISP_WS%\eigen-3.3.9\build-mingw\install folder): C:\> cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles" %VISP_WS%\eigen-3.3.9 \
-DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=%VISP_WS%\eigen-3.3.9\build-mingw\install
C:\> cmake --build . --config Release --target install -j4
%VISP_WS%\eigen-3.3.9\build-mingw\install folder.3. Complete Eigen3 installation
Now you have to complete Eigen3 installation setting some environment vars:
EIGEN_DIR environment variable. Start up a cmd Command Prompt and enter: C:\> setx Eigen3_DIR "%VISP_WS%\eigen-3.3.9\build-mingw\install\share\eigen3\cmake" C:\> exitwhere
%VISP_WS%\eigen-3.3.9\build-mingw\install is where you have installed Eigen3. Inside the folder %VISP_WS%\eigen-3.3.9\build-mingw\install\share\eigen3\cmake you should have a file named Eigen3Config.cmake.Path environment var since Eigen3 is a template that has no library.1. Get OpenCV
First you have to get OpenCV:
opencv-4.5.1-vc14_vc15.exe Win pack installer. The same procedure could be applied with all the previous OpenCV releases starting from 3.4.0 version.%VISP_WS%. 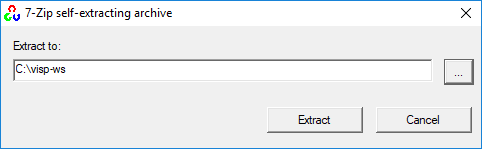
%VISP_WS%\opencv.%VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.1.%VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.1\build\x64\mingw.2. Configure, build and install OpenCV from source
cmd Command Prompt and create a build folder C:\> mkdir %VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.1\build-mingw C:\> cd %VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.1\build-mingw
VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.1\build. We disable also tests build in order to speed up the build process: C:\> cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles" ..\sources -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=%VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.1\build \
-DBUILD_TESTS=OFF -DBUILD_PERF_TESTS=OFF
C:\> cmake --build . --config Release --target install -j4
%VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.1\build folderOPENCV_ENABLE_ALLOCATOR_STATS=OFF you will get an gcc: error: long: No such file or directory. WITH_OPENCL_D3D11_NV=OFF you will get an OpenCL D3D11 build failure. 3. Complete OpenCV installation
Now you have to complete OpenCV installation setting some environment vars:
OpenCV_DIR environment variable. Start up a cmd Command Prompt and enter: C:\> setx OpenCV_DIR "%VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.1\build" C:\> exitwhere
%VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.1\build is where you have installed OpenCV. Inside this folder you should have a file named OpenCVConfig.cmake.Path environment variable. Open the "Edit environment variable" UI, and modify Path to add a new line with %VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.1\build\x64\mingw\bin.There are different ways to get ViSP source code.
visp-x.y.z.tar.gz or visp-x.y.z.zip is downloaded, uncompress the file in %VISP_WS%\visp\visp-x.y.z using for example WinRAR.visp-snapshot-yyyy-mm-dd.tar.gz is downloaded, uncompress the file in %VISP_WS%\visp\visp-x.y.z using for example WinRAR.git command line tool: C:\> cd %VISP_WS% C:\> git clone https://github.com/lagadic/visp.git
We suppose now that ViSP source is in %VISP_WS%\visp.
The goal of the configuration step is now to use CMake to produce a Visual Studio C++ solution file that will be located in %VISP_WS%/visp-build-mingw.
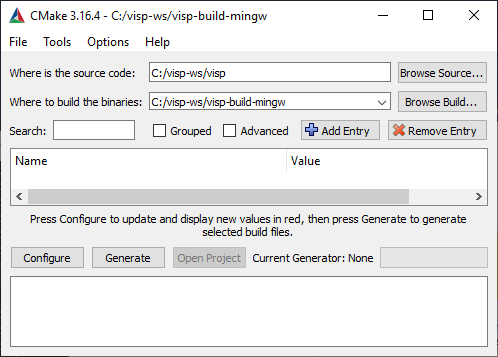
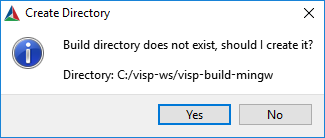
%VISP_WS%/visp-build-mingw folder.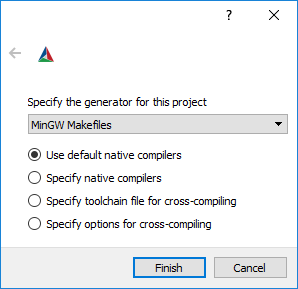
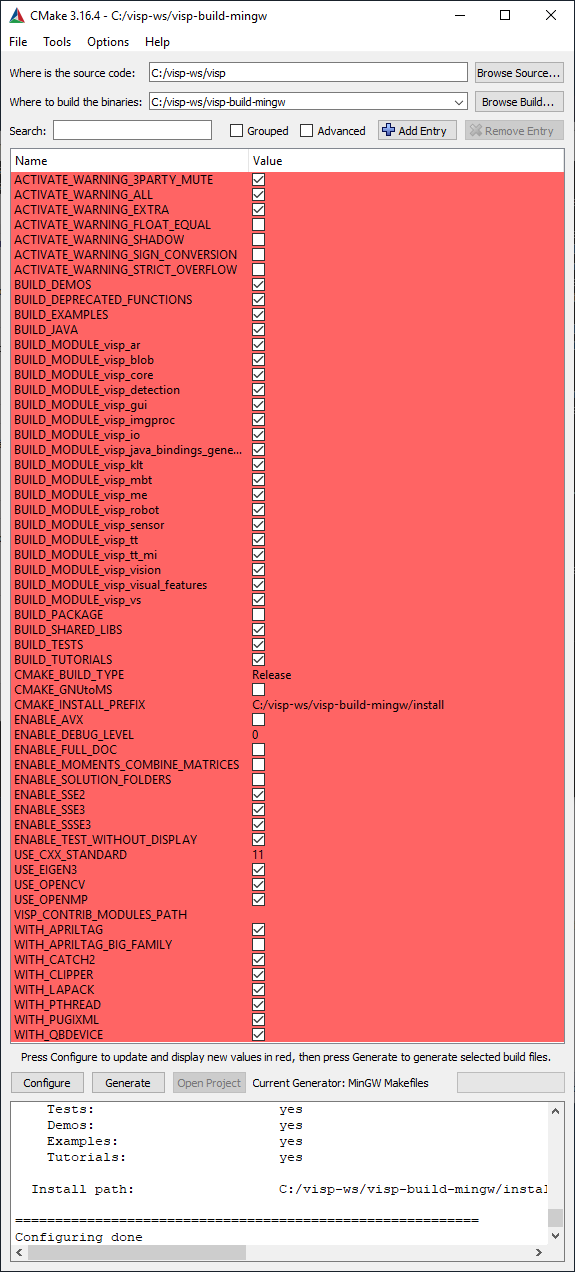
%VISP_WS%/visp-build-mingw/install. If you want to change the installation folder to C:/Program Files (x86)/ViSP, make sure that you have administrator privileges to write in that folder before modifying CMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX..dll extension). This is the default configuration that is recommended. If you want to create rather a static library (with .lib extension) you have to uncheck the BUILD_SHARED_LIBS option to disable DLL creation.
%VISP_WS%/visp-build-mingw folder you have the Makefile file that will be used by MinGW to build the whole project.cmd Command Prompt, change to %VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw folder and run mingw32-make: C:\> cd %VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw C:\> mingw32-make -j4
cmd Command Prompt run: C:\> mingw32-make -j4 install
%VISP_WS%/visp-build-mingw/install/x64/mingw/bin folder you will find ViSP DLL libraries corresponding to the build modules. 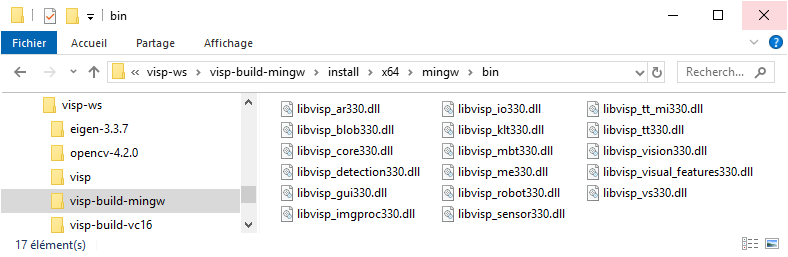
CMAKE_BUILD_TYPE is set to Debug, the library names are suffixed by "d".To build ViSP documentation, you have first to install Doxygen:
doxygen-1.8.20-setup.execmd Command Prompt and enter build directory C:\> cd %VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw
C:\> cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles" %VISP_WS%\visp
C:\> cmake --build . --config Release --target visp_doc
The generated documentation is then available in $VISP_WS/visp-build-mingw/doc/html/index.html
npm LTS version following these instructions, then install MathJax and build doc using: C:\> npm install mathjax C:\> cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles" %VISP_WS%\visp -DUSE_MATHJAX=ON C:\> cmake --build . --config Release --target visp_doc
ENABLE_FULL_DOC to ON like: C:\> cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles" %VISP_WS%\visp -DENABLE_FULL_DOC=ON C:\> cmake --build . --config Release --target visp_doc
Modify the Path var to add the path to ViSP dll libraries. To this end open the "Edit environment variable" UI, and modify Path to add a new line with %VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw\install\x64\mingw\bin.
In order to ease ViSP detection by CMake when ViSP is used as a 3rd party in an external project, like the one described in the Tutorial: How to create and build a project that uses ViSP and CMake on Unix or Windows, you may set VISP_DIR environment variable with the path to the VISPConfig.cmake file:
C:\> setx VISP_DIR "%VISP_WS%\visp-build-mingw\install" C:\> exit
Some ViSP examples and tests require a dataset that contains images, video, models that is not part of ViSP source code. This dataset is available in Github (https://github.com/lagadic/visp-images) or as a release in a separate archive named visp-images-x.y.z.zip. This archive could be downloaded from http://visp.inria.fr/download page. Note that ViSP tutorials are not using ViSP data set.
We give hereafter the two ways to get this data set:
1. Get data set release
visp-images-3.3.0.zip from https://visp.inria.fr/download and uncompress it in your workspace %VISP_WS%. 
VISP_INPUT_IMAGE_PATH environment variable to help ViSP examples and tests to detect automatically the location of the requested data. In our case, this variable should be set to %VISP_WS%\visp-images-3.3.0. Open a cmd Command Prompt and run C:\> setx VISP_INPUT_IMAGE_PATH %VISP_WS%\visp-images-3.3.0 C:\> exit
2. Get data set from github
C:\> cd %VISP_WS% C:\> git clone https://github.com/lagadic/visp-images.git
VISP_INPUT_IMAGE_PATH environment variable to help ViSP examples and tests to detect automatically the location of the requested data. In our case, this variable should be set to %VISP_WS%\visp-images. Open a cmd Command Prompt and run C:\> setx VISP_INPUT_IMAGE_PATH %VISP_WS%\visp-images C:\> exit
Test data set usage
From now, you can try to run ViSP examples and tests. For example, if you want to run %VISP_WS%\visp-build-vc15\example\device\display\Release\displayGDI.exe, open a cmd Command Prompt, enter in the right folder and run:
C:\> cd %VISP_WS%\visp-build-vc15\example\device\display\Release C:\> displayGDI.exe A click to close the windows... A click to display a cross... Cross position: 392, 306 A click to exit the program... Bye
Since all 3rd parties are optional you may have started to install only some of them. Imagine that you just installed a new third-party, or that you upgraded the version of this 3rd party. The next step is to go back to the build folder, configure ViSP with CMake to detect the newly installed third-party library and build again ViSP. This could be achieved with:
$ cd $VISP_WS/visp-build-mingw $ cmake ../visp
Here you can check the content of the ViSP-third-party.txt file and see if the newly installed 3rd party is well detected.
Finally, you need to rebuild ViSP with:
$ mingw32-make
After ViSP installation, you can remove installed material using:
$ cd $VISP_WS/visp-build-mingw $ mingw32-make uninstall
If you want to build only ViSP modules libraries, nor the examples, tutorials and tests:
$ cd $VISP_WS%/visp-build-mingw $ mingw32-make visp_modules
If you want to build a given module and all the dependencies:
$ cd $VISP_WS%/visp-build-mingw $ mingw32-make visp_<module_name>
For example to build the model-based tracker module named mbt, run:
$ cd $VISP_WS%/visp-build-mingw $ mingw32-make visp_mbt
To see which are the optional 3rd parties that are found during the configuration stage and that will be used by ViSP during the build you can have a look to the text file named ViSP-third-party.txt and located in VISP_WS%/visp-build-mingw. We provide hereafter an example of a possible content of this file that contains also build info.
$ type %VISP_WS%/visp-build-mingw/ViSP-third-party.txt
==========================================================
General configuration information for ViSP 3.3.1
Version control: 3.2.0-1289-g02f11a7de-dirty
Platform:
Timestamp: 2020-12-02T15:54:52Z
Host: Windows 10.0.17763 AMD64
CMake: 3.19.0
CMake generator: MinGW Makefiles
CMake build tool: C:/PROGRA~1/MINGW-~1/X86_64~1.0-P/mingw64/bin/mingw32-make.exe
Configuration: Release
C/C++:
Built as dynamic libs?: yes
C++ Compiler: C:/Program Files/mingw-w64/x86_64-8.1.0-posix-seh-rt_v6-rev0/mingw64/bin/g++.exe (ver 8.1.0)
C++ flags (Release): -Wall -Wextra -fopenmp -std=c++11 -fvisibility=hidden -msse2 -msse3 -mssse3 -O3 -DNDEBUG
C++ flags (Debug): -Wall -Wextra -fopenmp -std=c++11 -fvisibility=hidden -msse2 -msse3 -mssse3 -g
C Compiler: C:/Program Files/mingw-w64/x86_64-8.1.0-posix-seh-rt_v6-rev0/mingw64/bin/gcc.exe
C flags (Release): -Wall -Wextra -fopenmp -std=c++11 -fvisibility=hidden -msse2 -msse3 -mssse3 -O3 -DNDEBUG
C flags (Debug): -Wall -Wextra -fopenmp -std=c++11 -fvisibility=hidden -msse2 -msse3 -mssse3 -g
Linker flags (Release):
Linker flags (Debug):
ViSP modules:
To be built: core gui imgproc io java_bindings_generator klt me sensor ar blob robot visual_features vs vision detection mbt tt tt_mi
Disabled: -
Disabled by dependency: -
Unavailable: java
Windows RT support: no
Python (for build): NO
Java:
ant: NO
JNI: NO
Build options:
Build deprecated: yes
Build with moment combine: no
Mathematics:
Blas/Lapack: yes
\- Use MKL: no
\- Use OpenBLAS: no
\- Use Atlas: no
\- Use Netlib: no
\- Use GSL: no
\- Use Lapack (built-in): yes (ver 3.2.1)
Use Eigen3: yes (ver 3.3.8)
Use OpenCV: yes (ver 4.5.1)
Simulator:
Ogre simulator:
\- Use Ogre3D: no
\- Use OIS: no
Coin simulator:
\- Use Coin3D: no
\- Use SoWin: no
\- Use SoXt: no
\- Use SoQt: no
\- Use Qt5: no
\- Use Qt4: no
\- Use Qt3: no
Media I/O:
Use JPEG: no
Use PNG: no
\- Use ZLIB: no
Use OpenCV: yes (ver 4.5.1)
Use stb_image (built-in): no
Real robots:
Use Afma4: no
Use Afma6: no
Use Franka: no
Use Viper650: no
Use Viper850: no
Use Kinova Jaco: no
Use aria (Pioneer): no
Use PTU46: no
Use Biclops PTU: no
Use Flir PTU SDK: no
Use Parrot ARSDK: no
\-Use ffmpeg: no
Use Virtuose: no
Use qbdevice (built-in): yes (ver 2.6.0)
Use takktile2 (built-in): no
GUI:
Use X11: no
Use GTK: no
Use OpenCV: yes (ver 4.5.1)
Use GDI: no
Use Direct3D: no
Cameras:
Use DC1394-2.x: no
Use CMU 1394: no
Use V4L2: no
Use directshow: no
Use OpenCV: yes (ver 4.5.1)
Use Flycapture: no
Use Pylon: no
RGB-D sensors:
Use Realsense: no
Use Realsense2: no
Use Kinect: no
\- Use libfreenect: no
\- Use libusb-1: no
\- Use pthread: no
Use PCL: no
\- Use VTK: no
F/T sensors:
Use atidaq (built-in): no
Use comedi: no
Use IIT SDK: no
Detection:
Use zbar: no
Use dmtx: no
Use AprilTag (built-in): yes (ver 3.1.1)
\- Use AprilTag big family: no
Misc:
Use Clipper (built-in): yes (ver 6.4.2)
Use pugixml (built-in): yes (ver 1.9.0)
Use libxml2: no
Optimization:
Use OpenMP: yes
Use pthread: no
Use pthread (built-in): yes (ver 3.0.1)
Use cxx standard: 11
Documentation:
Use doxygen: yes
Tests and samples:
Use catch2 (built-in): yes (ver 2.9.2)
Tests: yes
Demos: yes
Examples: yes
Tutorials: yes
Install path: C:/visp-ws/visp-fspindle-build-mingw/install
==========================================================
This issue occurs with OpenCV 4.5.0 and is referenced here.
C:\>cmake --build . --config Release --target install ... [ 44%] Building RC object modules/core/CMakeFiles/opencv_core.dir/vs_version.rc.obj gcc: error: long: No such file or directory C:\PROGRA~1\MINGW-~1\X86_64~1.0-P\mingw64\bin\windres.exe: preprocessing failed. mingw32-make.exe[2]: *** [modules\core\CMakeFiles\opencv_core.dir\build.make:1494: modules/core/CMakeFiles/opencv_core.dir/vs_version.rc.obj] Error 1 mingw32-make.exe[1]: *** [CMakeFiles\Makefile2:1770: modules/core/CMakeFiles/opencv_core.dir/all] Error 2 mingw32-make.exe: *** [Makefile:181: all] Error 2
The workaround is to configure OpenCV build using cmake -DOPENCV_ENABLE_ALLOCATOR_STATS=OFF like:
C:\> cd %VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.0\build-mingw
C:\> cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles" ..\sources -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=%VISP_WS%\opencv-4.5.0\build \
-DBUILD_TESTS=OFF -DBUILD_PERF_TESTS=OFF -DWITH_OPENCL_D3D11_NV=OFF -DOPENCV_ENABLE_ALLOCATOR_STATS=OFF
C:\> cmake --build . --config Release --target install -j4
This issue occurs with OpenCV 4.1.1 and is referenced here.
If you encounter the following issue during OpenCV build:
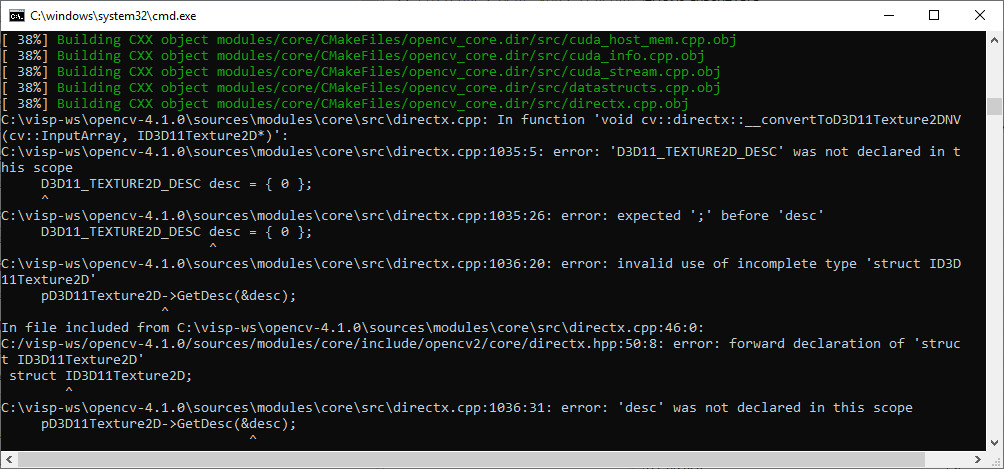
you have to disable OpenCL D3D11 support and restart a new build:
C:\> cd %VISP_WS%\opencv-4.1.1\build-mingw
C:\> cmake -G "MinGW Makefiles" ..\sources -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=%VISP_WS%\opencv-4.1.1\build \
-DWITH_OPENCL_D3D11_NV=OFF
C:\> cmake --build . --config Release --target install
If you encounter the following issue during CMake configuration
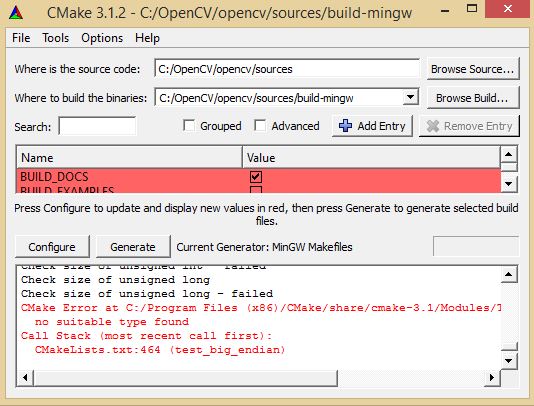
Edit %VISP_WS%\opencv-2.y.z\sources\CMakeLists.txt file, and line 464 replace:
test_big_endian(WORDS_BIGENDIAN)
by:
#test_big_endian(WORDS_BIGENDIAN) set(WORDS_BIGENDIAN 0)
If you encounter a build issue during libtiff build as given in the next image:
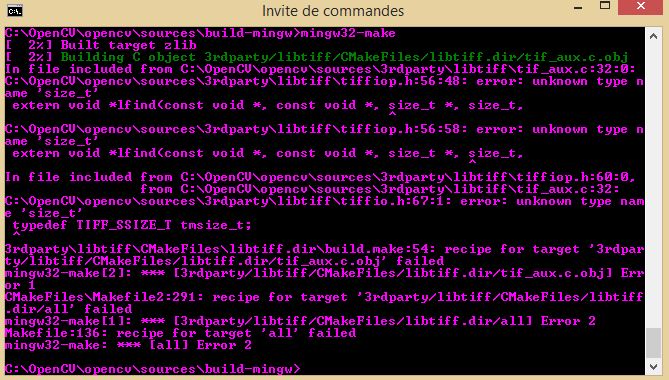
cd %VISP_WS%\opencv-2.y.z\sources\build-mingw C:\> mingw32-make
The following image shows the link issue that may appear when building OpenCV with MinGW:
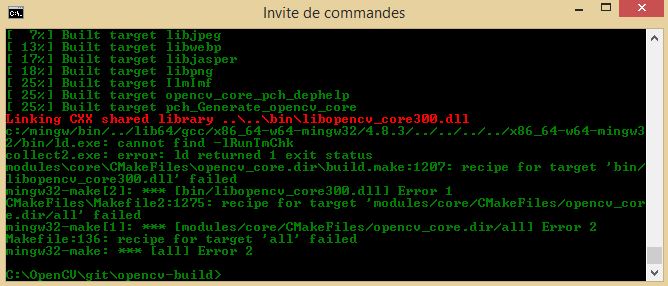
A work around is to configure OpenCV without ipp support turning WITH_IPP=OFF and then trying to build again.
This error that occurs with OpenCV 3.0.0 during cap_dshow.cpp build is known and reported as an issue in https://github.com/Itseez/opencv/pull/5282/commits.
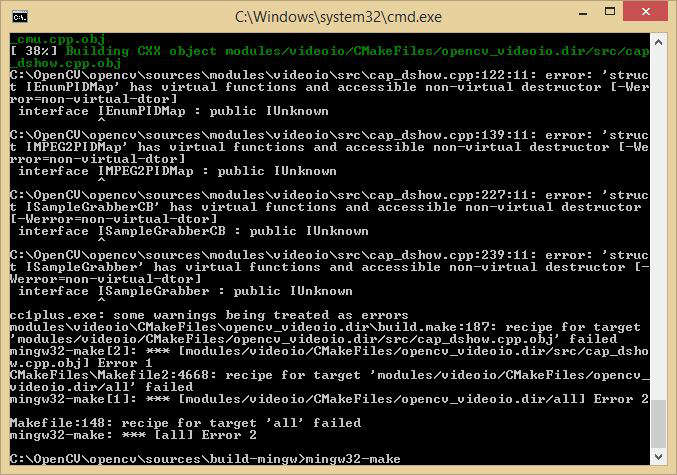
modules/videoio/src/cap_dshow.cpp by adding near line 96: #ifdef __MINGW32__ // MinGW does not understand COM interfaces #pragma GCC diagnostic ignored "-Wnon-virtual-dtor" #endif
%VISP_WS%\opencv-2.y.z\sources\cmake\OpenCVConfig.cmake, and line 89 replace: if(CMAKE_OPENCV_GCC_TARGET_MACHINE MATCHES "64")by:
if(OPENCV_GCC_TARGET_MACHINE MATCHES "64")
cmd Command Prompt to build and install OpenCV again: C:\> cd %VISP_WS%\opencv-2.y.z\sources\build-mingw C:\> mingw32-make install
When running mingw32-make if you get the following issue:
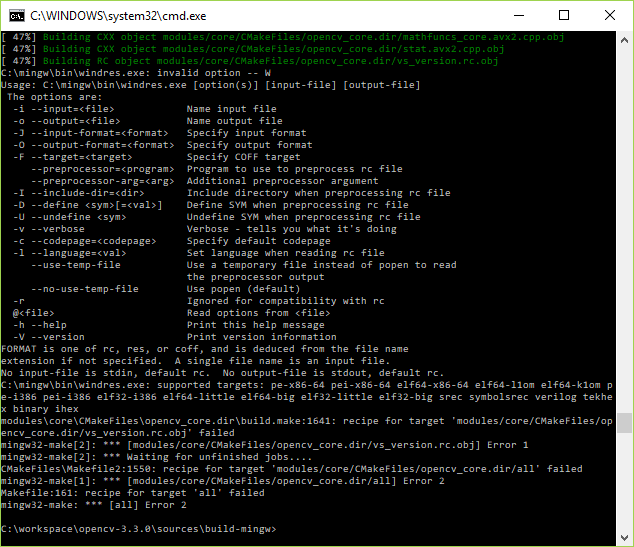
the workaround consists in:
ENABLE_PRECOMPILED_HEADERS cmake var OFF: 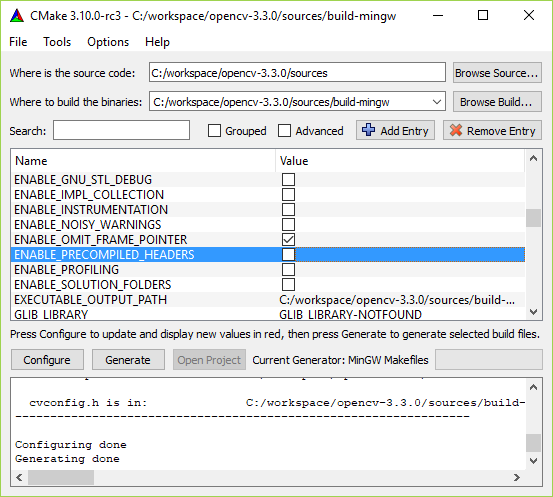
cmd Command Prompt run again mingw32-makeWhen running mingw32-make if you get the following issue:
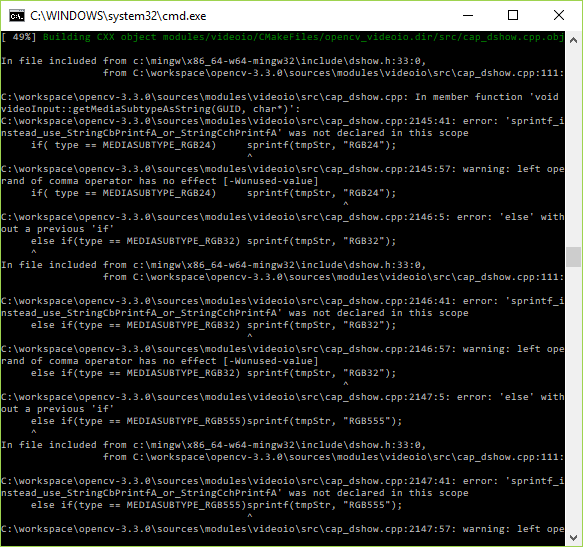
the workaround consists in:
%VISP_WS%/opencv-3.3.0/sources/modules/videoio/src/cap_dshow.cpp adding cmd Command Prompt run again mingw32-makeYou are now ready to see the next Tutorial: How to create and build a project that uses ViSP and CMake on Unix or Windows that will show you how to use ViSP as a 3rd party to build your own project.