 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.0.0
|
 |
Visual Servoing Platform
version 3.0.0
|
#include <visp3/robot/vpViper.h>
 Inheritance diagram for vpViper:
Inheritance diagram for vpViper:Static Public Attributes | |
| static const unsigned int | njoint = 6 |
Protected Attributes | |
| vpHomogeneousMatrix | eMc |
| vpTranslationVector | etc |
| vpRxyzVector | erc |
| double | a1 |
| double | d1 |
| double | a2 |
| double | a3 |
| double | d4 |
| double | d6 |
| double | c56 |
| vpColVector | joint_max |
| vpColVector | joint_min |
Friends | |
| VISP_EXPORT std::ostream & | operator<< (std::ostream &os, const vpViper &viper) |
Modelisation of the ADEPT Viper robot.
This robot has six degrees of freedom.
The non modified Denavit-Hartenberg representation of the robot is given in the table below, where  are the variable joint positions.
are the variable joint positions.
![\[ \begin{tabular}{|c|c|c|c|c|} \hline Joint & $a_i$ & $d_i$ & $\alpha_i$ & $\theta_i$ \\ \hline 1 & $a_1$ & $d_1$ & $-\pi/2$ & $q_1^*$ \\ 2 & $a_2$ & 0 & 0 & $q_2^*$ \\ 3 & $a_3$ & 0 & $-\pi/2$ & $q_3^* - \pi$ \\ 4 & 0 & $d_4$ & $\pi/2$ & $q_4^*$ \\ 5 & 0 & 0 & $-\pi/2$ & $q_5^*$ \\ 6 & 0 & 0 & 0 & $q_6^*-\pi$ \\ 7 & 0 & $d_6$ & 0 & 0 \\ \hline \end{tabular} \]](form_555.png)
In this modelisation, different frames have to be considered.
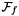 : the reference frame, also called world frame,
: the reference frame, also called world frame,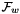 : the wrist frame located at the intersection of the last three rotations, with
: the wrist frame located at the intersection of the last three rotations, with 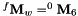 ,
,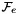 : the end-effector frame, with
: the end-effector frame, with 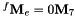 ,
,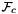 : the camera frame, with
: the camera frame, with 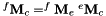 where
where 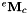 is the result of a calibration stage.
is the result of a calibration stage.The forward kinematics of the robot is implemented in get_fMw(), get_fMe() and get_fMc().
The robot forward jacobian used to compute the cartesian velocities from joint ones is given and implemented in get_fJw(), get_fJe() and get_eJe().
| vpViper::vpViper | ( | ) |
Default constructor.
Definition at line 66 of file vpViper.cpp.
References a1, a2, a3, c56, d1, d4, d6, eMc, vpHomogeneousMatrix::eye(), joint_max, joint_min, njoint, vpMath::rad(), and vpColVector::resize().
| void vpViper::get_cMe | ( | vpHomogeneousMatrix & | cMe | ) | const |
Get the geometric transformation between the camera frame and the end-effector frame. This transformation is constant and correspond to the extrinsic camera parameters estimated by calibration.
| cMe | : Transformation between the camera frame and the end-effector frame. |
Definition at line 927 of file vpViper.cpp.
References eMc, and vpHomogeneousMatrix::inverse().
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::get_cMe(), vpRobotViper850::get_cMe(), vpRobotViper650::get_cMe(), get_cVe(), vpSimulatorViper850::get_cVe(), vpRobotViper850::get_cVe(), and vpRobotViper650::get_cVe().
| void vpViper::get_cVe | ( | vpVelocityTwistMatrix & | cVe | ) | const |
Get the twist transformation 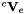 from camera frame to end-effector frame. This transformation allows to compute a velocity expressed in the end-effector frame into the camera frame.
from camera frame to end-effector frame. This transformation allows to compute a velocity expressed in the end-effector frame into the camera frame.
![\[ ^c{\bf V}_e = \left(\begin{array}{cc} ^c{\bf R}_e & [^c{\bf t}_e]_\times ^c{\bf R}_e\\ {\bf 0}_{3\times 3} & ^c{\bf R}_e \end{array} \right) \]](form_613.png)
| cVe | : Twist transformation 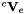 . . |
Definition at line 948 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpVelocityTwistMatrix::buildFrom(), and get_cMe().
| void vpViper::get_eJe | ( | const vpColVector & | q, |
| vpMatrix & | eJe | ||
| ) | const |
Get the robot jacobian 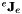 which gives the velocity of the origin of the end-effector frame expressed in end-effector frame.
which gives the velocity of the origin of the end-effector frame expressed in end-effector frame.
![\[ {^e}{\bf J}_e = \left[\begin{array}{cc} {^w}{\bf R}_f & {[{^e}{\bf t}_w}]_\times \; {^w}{\bf R}_f \\ 0_{3\times3} & {^w}{\bf R}_f \end{array} \right] \; {^f}{\bf J}_w \]](form_614.png)
| q | : A six-dimension vector that contains the joint positions of the robot expressed in radians. |
| eJe | : Robot jacobian 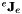 that express the velocity of the end-effector in the robot end-effector frame. that express the velocity of the end-effector in the robot end-effector frame. |
Definition at line 981 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpHomogeneousMatrix::extract(), get_fJw(), get_fMw(), get_wMe(), vpRotationMatrix::inverse(), vpHomogeneousMatrix::inverse(), and vpTranslationVector::skew().
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::computeArticularVelocity(), vpSimulatorViper850::get_eJe(), vpRobotViper650::get_eJe(), vpRobotViper850::get_eJe(), and vpSimulatorViper850::getVelocity().
| void vpViper::get_eMc | ( | vpHomogeneousMatrix & | eMc_ | ) | const |
Get the geometric transformation between the end-effector frame and the camera frame. This transformation is constant and correspond to the extrinsic camera parameters estimated by calibration.
| eMc_ | : Transformation between the the end-effector frame and the camera frame. |
Definition at line 910 of file vpViper.cpp.
References eMc.
Referenced by getInverseKinematics().
| void vpViper::get_fJe | ( | const vpColVector & | q, |
| vpMatrix & | fJe | ||
| ) | const |
Get the robot jacobian 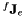 which gives the velocity of the origin of the end-effector frame expressed in the robot reference frame also called fix frame.
which gives the velocity of the origin of the end-effector frame expressed in the robot reference frame also called fix frame.
![\[ {^f}{\bf J}_e = \left[\begin{array}{cc} I_{3\times3} & [{^f}{\bf R}_w \; {^e}{\bf t}_w]_\times \\ 0_{3\times3} & I_{3\times3} \end{array} \right] {^f}{\bf J}_w \]](form_619.png)
| q | : A six-dimension vector that contains the joint positions of the robot expressed in radians. |
| fJe | : Robot jacobian 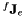 that express the velocity of the end-effector in the robot reference frame. that express the velocity of the end-effector in the robot reference frame. |
Definition at line 1173 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpHomogeneousMatrix::extract(), get_fJw(), get_fMw(), get_wMe(), and vpHomogeneousMatrix::inverse().
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::computeArticularVelocity(), vpSimulatorViper850::get_fJe(), vpRobotViper650::get_fJe(), vpRobotViper850::get_fJe(), and vpSimulatorViper850::getVelocity().
| void vpViper::get_fJw | ( | const vpColVector & | q, |
| vpMatrix & | fJw | ||
| ) | const |
Get the robot jacobian 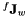 which express the velocity of the origin of the wrist frame in the robot reference frame also called fix frame.
which express the velocity of the origin of the wrist frame in the robot reference frame also called fix frame.
![\[ {^f}J_w = \left(\begin{array}{cccccc} J_{11} & J_{12} & J_{13} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ J_{21} & J_{22} & J_{23} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & J_{32} & J_{33} & 0 & 0 & 0 \\ 0 & -s1 & -s1 & c1s23 & J_{45} & J_{46} \\ 0 & c1 & c1 & s1s23 & J_{55} & J_{56} \\ 1 & 0 & 0 & c23 & s23s4 & J_{56} \\ \end{array} \right) \]](form_616.png)
with
![\[ \begin{array}{l} J_{11} = -s1(-c23a3+s23d4+a1+a2c2) \\ J_{21} = c1(-c23a3+s23d4+a1+a2c2) \\ J_{12} = c1(s23a3+c23d4-a2s2) \\ J_{22} = s1(s23a3+c23d4-a2s2) \\ J_{32} = c23a3-s23d4-a2c2 \\ J_{13} = c1(a3(s2c3+c2s3)+(-s2s3+c2c3)d4)\\ J_{23} = s1(a3(s2c3+c2s3)+(-s2s3+c2c3)d4)\\ J_{33} = -a3(s2s3-c2c3)-d4(s2c3+c2s3)\\ J_{45} = -c23c1s4-s1c4\\ J_{55} = c1c4-c23s1s4\\ J_{46} = (c1c23c4-s1s4)s5+c1s23c5\\ J_{56} = (s1c23c4+c1s4)s5+s1s23c5\\ J_{66} = -s23c4s5+c23c5\\ \end{array} \]](form_617.png)
| q | : A six-dimension vector that contains the joint positions of the robot expressed in radians. |
| fJw | : Robot jacobian 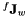 that express the velocity of the point w (origin of the wrist frame) in the robot reference frame. that express the velocity of the point w (origin of the wrist frame) in the robot reference frame. |
Definition at line 1067 of file vpViper.cpp.
References a1, a2, a3, d4, and vpArray2D< Type >::resize().
| vpHomogeneousMatrix vpViper::get_fMc | ( | const vpColVector & | q | ) | const |
Compute the forward kinematics (direct geometric model) as an homogeneous matrix.
By forward kinematics we mean here the position and the orientation of the camera relative to the base frame given the joint positions of all the six joints.
![\[ ^f{\bf M}_c = ^f{\bf M}_e \; ^e{\bf M}_c \]](form_604.png)
This method is the same than getForwardKinematics(const vpColVector & q).
| q | : Vector of six joint positions expressed in radians. |
Definition at line 611 of file vpViper.cpp.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), getForwardKinematics(), vpSimulatorViper850::getPosition(), vpRobotViper850::getVelocity(), vpRobotViper650::getVelocity(), vpSimulatorViper850::setPosition(), vpRobotViper850::setPosition(), and vpRobotViper650::setPosition().
| void vpViper::get_fMc | ( | const vpColVector & | q, |
| vpHomogeneousMatrix & | fMc | ||
| ) | const |
Compute the forward kinematics (direct geometric model) as an homogeneous matrix.
By forward kinematics we mean here the position and the orientation of the camera relative to the base frame given the six joint positions.
![\[ ^f{\bf M}_c = ^f{\bf M}_e \; {^e}{\bf M}_c \]](form_605.png)
| q | : Vector of six joint positions expressed in radians. |
| fMc | The homogeneous matrix 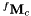 corresponding to the direct geometric model which expresses the transformation between the fix frame and the camera frame. corresponding to the direct geometric model which expresses the transformation between the fix frame and the camera frame. |
Definition at line 641 of file vpViper.cpp.
| void vpViper::get_fMe | ( | const vpColVector & | q, |
| vpHomogeneousMatrix & | fMe | ||
| ) | const |
Compute the forward kinematics (direct geometric model) as an homogeneous matrix 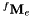 .
.
By forward kinematics we mean here the position and the orientation of the end effector with respect to the base frame given the motor positions of all the six joints.
![\[ {^f}M_e = \left(\begin{array}{cccc} r_{11} & r_{12} & r_{13} & t_x \\ r_{21} & r_{22} & r_{23} & t_y \\ r_{31} & r_{32} & r_{33} & t_z \\ \end{array} \right) \]](form_608.png)
with
![\[ \begin{array}{l} r_{11} = c1(c23(c4c5c6-s4s6)-s23s5c6)-s1(s4c5c6+c4s6) \\ r_{21} = -s1(c23(-c4c5c6+s4s6)+s23s5c6)+c1(s4c5c6+c4s6) \\ r_{31} = s23(s4s6-c4c5c6)-c23s5c6 \\ \\ r_{12} = -c1(c23(c4c5s6+s4c6)-s23s5s6)+s1(s4c5s6-c4c6)\\ r_{22} = -s1(c23(c4c5s6+s4c6)-s23s5s6)-c1(s4c5s6-c4c6)\\ r_{32} = s23(c4c5s6+s4c6)+c23s5s6\\ \\ r_{13} = c1(c23c4s5+s23c5)-s1s4s5\\ r_{23} = s1(c23c4s5+s23c5)+c1s4s5\\ r_{33} = -s23c4s5+c23c5\\ \\ t_x = c1(c23(c4s5d6-a3)+s23(c5d6+d4)+a1+a2c2)-s1s4s5d6\\ t_y = s1(c23(c4s5d6-a3)+s23(c5d6+d4)+a1+a2c2)+c1s4s5d6\\ t_z = s23(a3-c4s5d6)+c23(c5d6+d4)-a2s2+d1\\ \end{array} \]](form_609.png)
| q | : A 6-dimension vector that contains the 6 joint positions expressed in radians. |
| fMe | The homogeneous matrix 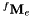 corresponding to the direct geometric model which expresses the transformation between the fix frame and the end effector frame. corresponding to the direct geometric model which expresses the transformation between the fix frame and the end effector frame. |
Note that this transformation can also be computed by considering the wrist frame 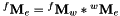 .
.
Definition at line 728 of file vpViper.cpp.
References a1, a2, a3, d1, d4, and d6.
Referenced by get_fMc().
| void vpViper::get_fMw | ( | const vpColVector & | q, |
| vpHomogeneousMatrix & | fMw | ||
| ) | const |
Compute the transformation between the fix frame and the wrist frame. The wrist frame is located on the intersection of the 3 last rotations.
| q | : A 6-dimension vector that contains the 6 joint positions expressed in radians. |
| fMw | The homogeneous matrix corresponding to the transformation between the fix frame and the wrist frame (fMw). |
![\[ {^f}M_w = \left(\begin{array}{cccc} r_{11} & r_{12} & r_{13} & t_x \\ r_{21} & r_{22} & r_{23} & t_y \\ r_{31} & r_{32} & r_{33} & t_z \\ \end{array} \right) \]](form_611.png)
with
![\[ \begin{array}{l} r_{11} = c1(c23(c4c5c6-s4s6)-s23s5c6)-s1(s4c5c6+c4s6) \\ r_{21} = -s1(c23(-c4c5c6+s4s6)+s23s5c6)+c1(s4c5c6+c4s6) \\ r_{31} = s23(s4s6-c4c5c6)-c23s5c6 \\ \\ r_{12} = -c1(c23(c4c5s6+s4c6)-s23s5s6)+s1(s4c5s6-c4c6)\\ r_{22} = -s1(c23(c4c5s6+s4c6)-s23s5s6)-c1(s4c5s6-c4c6)\\ r_{32} = s23(c4c5s6+s4c6)+c23s5s6\\ \\ r_{13} = c1(c23c4s5+s23c5)-s1s4s5\\ r_{23} = s1(c23c4s5+s23c5)+c1s4s5\\ r_{33} = -s23c4s5+c23c5\\ \\ t_x = c1(-c23a3+s23d4+a1+a2c2)\\ t_y = s1(-c23a3+s23d4+a1+a2c2)\\ t_z = s23a3+c23d4-a2s2+d1\\ \end{array} \]](form_612.png)
Definition at line 824 of file vpViper.cpp.
| void vpViper::get_wMe | ( | vpHomogeneousMatrix & | wMe | ) | const |
Return the transformation between the wrist frame and the end-effector. The wrist frame is located on the intersection of the 3 last rotations.
| wMe | The homogeneous matrix corresponding to the transformation between the wrist frame and the end-effector frame (wMe). |
Definition at line 889 of file vpViper.cpp.
References d6, and vpHomogeneousMatrix::eye().
Referenced by get_eJe(), get_fJe(), and getInverseKinematics().
| double vpViper::getCoupl56 | ( | ) | const |
Return the coupling factor between join 5 and joint 6.
This factor should be only useful when motor positions are considered. Since the positions returned by the robot are joint positions which takes into account the coupling factor, it has not to be considered in the modelization of the robot.
Definition at line 1244 of file vpViper.cpp.
References c56.
| vpHomogeneousMatrix vpViper::getForwardKinematics | ( | const vpColVector & | q | ) | const |
Compute the forward kinematics (direct geometric model) as an homogeneous matrix.
By forward kinematics we mean here the position and the orientation of the camera relative to the base frame given the six joint positions.
This method is the same than get_fMc(const vpColVector & q).
| q | : A six dimension vector corresponding to the robot joint positions expressed in radians. |
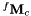 corresponding to the direct geometric model which expresses the transformation between the base frame and the camera frame.
corresponding to the direct geometric model which expresses the transformation between the base frame and the camera frame.Definition at line 125 of file vpViper.cpp.
References get_fMc().
| unsigned int vpViper::getInverseKinematics | ( | const vpHomogeneousMatrix & | fMc, |
| vpColVector & | q, | ||
| const bool & | verbose = false |
||
| ) | const |
Compute the inverse kinematics (inverse geometric model).
By inverse kinematics we mean here the six joint values given the position and the orientation of the camera frame relative to the base frame.
| fMc | : Homogeneous matrix 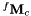 describing the transformation from base frame to the camera frame. describing the transformation from base frame to the camera frame. |
| q | : In input, a six dimension vector corresponding to the current joint positions expressed in radians. In output, the solution of the inverse kinematics, ie. the joint positions corresponding to 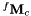 . . |
| verbose | : Add extra printings. |
The code below shows how to compute the inverse geometric model:
Definition at line 573 of file vpViper.cpp.
References get_eMc(), get_wMe(), getInverseKinematicsWrist(), and vpHomogeneousMatrix::inverse().
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::initialiseCameraRelativeToObject(), vpSimulatorViper850::setPosition(), vpRobotViper850::setPosition(), and vpRobotViper650::setPosition().
| unsigned int vpViper::getInverseKinematicsWrist | ( | const vpHomogeneousMatrix & | fMw, |
| vpColVector & | q, | ||
| const bool & | verbose = false |
||
| ) | const |
Compute the inverse kinematics (inverse geometric model).
By inverse kinematics we mean here the six joint values given the position and the orientation of the camera frame relative to the base frame.
| fMw | : Homogeneous matrix 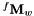 describing the transformation from base frame to the wrist frame. describing the transformation from base frame to the wrist frame. |
| q | : In input, a six dimension vector corresponding to the current joint positions expressed in radians. In output, the solution of the inverse kinematics, ie. the joint positions corresponding to 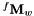 . . |
| verbose | : Add extra printings. |
The code below shows how to compute the inverse geometric model:
Definition at line 228 of file vpViper.cpp.
References a1, a2, a3, d1, d4, vpArray2D< Type >::getRows(), njoint, vpMath::rad(), vpColVector::resize(), and vpMath::sqr().
Referenced by getInverseKinematics().
| vpColVector vpViper::getJointMax | ( | ) | const |
Get maximal joint values.
Definition at line 1228 of file vpViper.cpp.
References joint_max.
| vpColVector vpViper::getJointMin | ( | ) | const |
Get minimal joint values.
Definition at line 1215 of file vpViper.cpp.
References joint_min.
|
virtual |
Set the geometric transformation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame (commonly a camera).
| eMc_ | : Transformation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame. |
Reimplemented in vpRobotViper650.
Definition at line 1258 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpRxyzVector::buildFrom(), eMc, erc, etc, and vpHomogeneousMatrix::extract().
Referenced by vpViper650::init(), vpViper650::parseConfigFile(), and vpRobotViper650::set_eMc().
|
virtual |
Set the geometric transformation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame (commonly a camera frame).
| etc_ | : Translation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame. |
| erc_ | : Rotation between the end-effector frame and the tool frame using the Euler angles in radians with the XYZ convention. |
Reimplemented in vpRobotViper650.
Definition at line 1277 of file vpViper.cpp.
References vpHomogeneousMatrix::buildFrom(), eMc, erc, and etc.
|
friend |
Print on the output stream os the robot parameters (joint min/max, coupling factor between axis 5 and 6, hand-to-eye constant homogeneous matrix 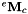 .
.
| os | : Output stream. |
| viper | : Robot parameters. |
Definition at line 1294 of file vpViper.cpp.
|
protected |
Definition at line 151 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), get_fJw(), get_fMe(), get_fMw(), getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpSimulatorViper850::singularityTest(), vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850::vpViper850().
|
protected |
for joint 2
Definition at line 152 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), get_fJw(), get_fMe(), get_fMw(), getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpSimulatorViper850::singularityTest(), vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850::vpViper850().
|
protected |
for joint 3
Definition at line 153 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), get_fJw(), get_fMe(), get_fMw(), getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpSimulatorViper850::singularityTest(), vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850::vpViper850().
|
protected |
Mechanical coupling between joint 5 and joint 6.
Definition at line 156 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by getCoupl56(), vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850::vpViper850().
|
protected |
for joint 1
Definition at line 151 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), get_fMe(), get_fMw(), getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850::vpViper850().
|
protected |
for joint 4
Definition at line 154 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), get_fJw(), get_fMe(), get_fMw(), getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpSimulatorViper850::singularityTest(), vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850::vpViper850().
|
protected |
for joint 6
Definition at line 155 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::compute_fMi(), get_fMe(), get_wMe(), vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850::vpViper850().
|
protected |
End effector to camera transformation.
Definition at line 145 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpSimulatorViper850::computeArticularVelocity(), get_cMe(), get_eMc(), get_fMc(), vpSimulatorViper850::getVelocity(), vpViper850::init(), vpViper650::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpViper850::parseConfigFile(), set_eMc(), and vpViper().
|
protected |
Definition at line 148 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpViper850::init(), vpViper650::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpRobotViper850::init(), vpViper850::parseConfigFile(), set_eMc(), and vpRobotViper650::set_eMc().
|
protected |
Definition at line 147 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpViper850::init(), vpViper650::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpRobotViper850::init(), vpViper850::parseConfigFile(), set_eMc(), and vpRobotViper650::set_eMc().
|
protected |
Definition at line 159 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by getJointMax(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpRobotViper850::init(), vpRobotViper650::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::isInJointLimit(), vpSimulatorViper850::setJointLimit(), vpSimulatorViper850::updateArticularPosition(), vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850::vpViper850().
|
protected |
Definition at line 160 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by getJointMin(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpRobotViper850::init(), vpRobotViper650::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::isInJointLimit(), vpSimulatorViper850::setJointLimit(), vpSimulatorViper850::updateArticularPosition(), vpViper(), vpViper650::vpViper650(), and vpViper850::vpViper850().
|
static |
Number of joint.
Definition at line 142 of file vpViper.h.
Referenced by vpRobotViper650::get_eJe(), vpRobotViper850::get_eJe(), vpRobotViper850::get_fJe(), vpRobotViper650::get_fJe(), vpRobotViper850::getDisplacement(), vpRobotViper650::getDisplacement(), getInverseKinematicsWrist(), vpSimulatorViper850::init(), vpSimulatorViper850::readPosFile(), vpRobotViper850::readPosFile(), vpRobotViper650::readPosFile(), vpRobotViper850::setPosition(), vpRobotViper650::setPosition(), vpRobotViper850::setVelocity(), vpRobotViper650::setVelocity(), and vpViper().