Example that shows how to control the Pioneer mobile robot by IBVS visual servoing with respect to a segment. The segment consists in two horizontal dots. The current visual features that are used are 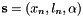 . The desired one are
. The desired one are 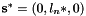 , with:
, with:
The depth of the points is estimated from the surface of the blob.
#include <iostream>
#include <visp3/core/vpConfig.h>
#include <visp3/robot/vpRobotPioneer.h>
#include <visp3/blob/vpDot2.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpCameraParameters.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpHomogeneousMatrix.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpImage.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpVelocityTwistMatrix.h>
#include <visp3/gui/vpDisplayGDI.h>
#include <visp3/gui/vpPlot.h>
#include <visp3/robot/vpPioneerPan.h>
#include <visp3/robot/vpRobotBiclops.h>
#include <visp3/sensor/vp1394CMUGrabber.h>
#include <visp3/sensor/vp1394TwoGrabber.h>
#include <visp3/sensor/vpV4l2Grabber.h>
#include <visp3/visual_features/vpFeatureBuilder.h>
#include <visp3/visual_features/vpFeatureSegment.h>
#include <visp3/vs/vpServo.h>
#include <visp3/gui/vpDisplayX.h>
#define USE_REAL_ROBOT
#define USE_PLOTTER
#undef VISP_HAVE_V4L2 // To use a firewire camera
#if defined(VISP_HAVE_PIONEER) && defined(VISP_HAVE_BICLOPS)
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
#if defined(VISP_HAVE_DC1394) || defined(VISP_HAVE_V4L2) || defined(VISP_HAVE_CMU1394)
#if defined(VISP_HAVE_X11) || defined(VISP_HAVE_GDI)
try {
double lambda = 0.1;
double coef = 1.2 / 13.0;
double L = 0.21;
double Z_d = 0.8;
bool normalized = true;
double Y_d = -.11;
qm = 0;
double qm_pan = 0;
#ifdef USE_REAL_ROBOT
q = 0;
qm_pan = qm[0];
ArArgumentParser parser(&argc, argv);
parser.loadDefaultArguments();
ArRobotConnector robotConnector(&parser, &pioneer);
if (!robotConnector.connectRobot()) {
ArLog::log(ArLog::Terse, "Could not connect to the pioneer robot.");
if (parser.checkHelpAndWarnUnparsed()) {
Aria::logOptions();
Aria::exit(1);
}
}
if (!Aria::parseArgs()) {
Aria::logOptions();
Aria::shutdown();
return false;
}
sleep(3);
std::cout << "Pioneer robot connected" << std::endl;
#endif
#if defined(VISP_HAVE_V4L2)
#elif defined(VISP_HAVE_DC1394)
#elif defined(VISP_HAVE_CMU1394)
#endif
#if defined(VISP_HAVE_X11)
#elif defined(VISP_HAVE_GDI)
#endif
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
}
std::cout << "cVe: \n" << cVe << std::endl;
std::cout << "eJe: \n" << eJe << std::endl;
0);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
}
double surface[2];
double Z[2];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
surface[i] = 1. / sqrt(dot[i].m00 / (cam.
get_px() * cam.
get_py()));
Z[i] = coef * surface[i];
}
s_segment_d(normalized);
s_segment.setZ1(Z[0]);
s_segment.setZ2(Z[1]);
s_segment.setZ1(P[0].get_Z());
s_segment.setZ2(P[1].get_Z());
#ifdef USE_PLOTTER
vpPlot graph(2, 500, 500, 700, 10,
"Curves...");
#endif
try {
unsigned int iter = 0;
while (1) {
#ifdef USE_REAL_ROBOT
#endif
qm_pan = qm[0];
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++)
dot[i].track(I);
for (int i = 0; i < 2; i++) {
surface[i] = 1. / sqrt(dot[i].m00 / (cam.
get_px() * cam.
get_py()));
Z[i] = coef * surface[i];
}
s_segment.setZ1(Z[0]);
s_segment.setZ2(Z[1]);
std::cout <<
"Warning: task is of rank " << task.
getTaskRank() << std::endl;
#ifdef USE_PLOTTER
#endif
#ifdef USE_REAL_ROBOT
v_pioneer[0] = v[0];
v_pioneer[1] = v[1];
v_biclops[0] = v[2];
v_biclops[1] = 0;
std::cout <<
"Send velocity to the pionner: " << v_pioneer[0] <<
" m/s " <<
vpMath::deg(v_pioneer[1])
<< " deg/s" << std::endl;
std::cout <<
"Send velocity to the biclops head: " <<
vpMath::deg(v_biclops[0]) <<
" deg/s" << std::endl;
#endif
break;
iter++;
}
} catch (...) {
}
#ifdef USE_REAL_ROBOT
std::cout << "Ending robot thread..." << std::endl;
pioneer.stopRunning();
pioneer.waitForRunExit();
#endif
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
std::cout << "Catch an exception: " << e << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
#endif
#endif
}
#else
int main()
{
std::cout << "ViSP is not able to control the Pioneer robot" << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
#endif


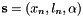 . The desired one are
. The desired one are 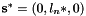 , with:
, with: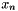 the normalized abscisse of the point corresponding to segment
the normalized abscisse of the point corresponding to segment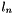 the normalized segment length
the normalized segment length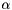 the segment orientation.
the segment orientation.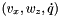 , the translational and rotational velocity of the mobile platform at point M located at the middle between the two wheels, the head pan velocity respectively.
, the translational and rotational velocity of the mobile platform at point M located at the middle between the two wheels, the head pan velocity respectively.