This tutorial will show how to use Blender , a free and open source 3D creation suite, to generate color and depth images from a virtual camera and get ground truth camera poses.
The configuration used for this tutorial is:
Ubuntu 16.04
Blender 2.79b
Warning You are advised to know how to use the basic tools of Blender before reading this tutorial. Some non-exhaustive links:
Note that all the material (source code, input video, CAD model or XML settings files) described and used in this tutorial is part of ViSP source code and could be downloaded using the following command:
In ViSP and in the computer vision community, camera intrinsic parameters are the following:
focal length
principal point
(plus the distortion coefficients)
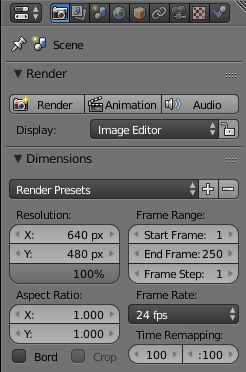
In Blender, you will have to set the camera resolution, generally 640x480 to have a VGA camera resolution:
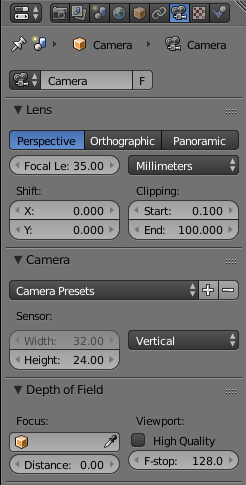
Focal length can be set with the camera panel by changing the focal length and/or the sensor size:
The relation is the following:
The Python script to get the camera intrinsic parameters is:
import bpy
from mathutils import Matrix
def get_calibration_matrix_K_from_blender(camd):
f_in_mm = camd.lens
scene = bpy.context.scene
resolution_x_in_px = scene.render.resolution_x
resolution_y_in_px = scene.render.resolution_y
scale = scene.render.resolution_percentage / 100
sensor_width_in_mm = camd.sensor_width
sensor_height_in_mm = camd.sensor_height
pixel_aspect_ratio = scene.render.pixel_aspect_x / scene.render.pixel_aspect_y
if (camd.sensor_fit == 'VERTICAL' ):
s_u = resolution_x_in_px * scale / sensor_width_in_mm / pixel_aspect_ratio
s_v = resolution_y_in_px * scale / sensor_height_in_mm
else :
pixel_aspect_ratio = scene.render.pixel_aspect_x / scene.render.pixel_aspect_y
s_u = resolution_x_in_px * scale / sensor_width_in_mm
s_v = resolution_y_in_px * scale * pixel_aspect_ratio / sensor_height_in_mm
alpha_u = f_in_mm * s_u
alpha_v = f_in_mm * s_v
u_0 = resolution_x_in_px*scale / 2
v_0 = resolution_y_in_px*scale / 2
skew = 0
K = Matrix(
((alpha_u, skew, u_0),
( 0 , alpha_v, v_0),
( 0 , 0, 1 )))
return K
if __name__ == "__main__" :
K = get_calibration_matrix_K_from_blender(bpy.data.objects['Camera' ].data)
print(K)
On Ubuntu, to run the Python script:
launch Blender from a terminal
split or switch from 3D View to Text Editor
open the Python script file
click on Run Script
You should get something similar to:
<Matrix 3x3 (700.0000, 0.0000, 320.0000)
( 0.0000, 700.0000, 240.0000)
( 0.0000, 0.0000, 1.0000)>
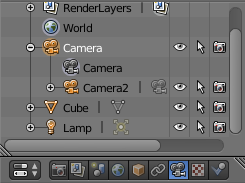
Warning In Blender 2.79b, you may need to switch the Sensor Fit from Auto to Vertical to change the Sensor Height to be compatible with a 4/3 ratio and have Note The principal point is always in the middle of the image here. To generate the depth map, add a second camera and set the appropriate parameters to match the desired intrinsic parameters. Then select one camera (the child object) and the other one (the parent object) and hit Ctrl + P to parent them. This way, the two cameras will be linked when you will move the cameras.
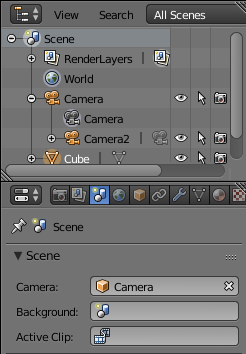
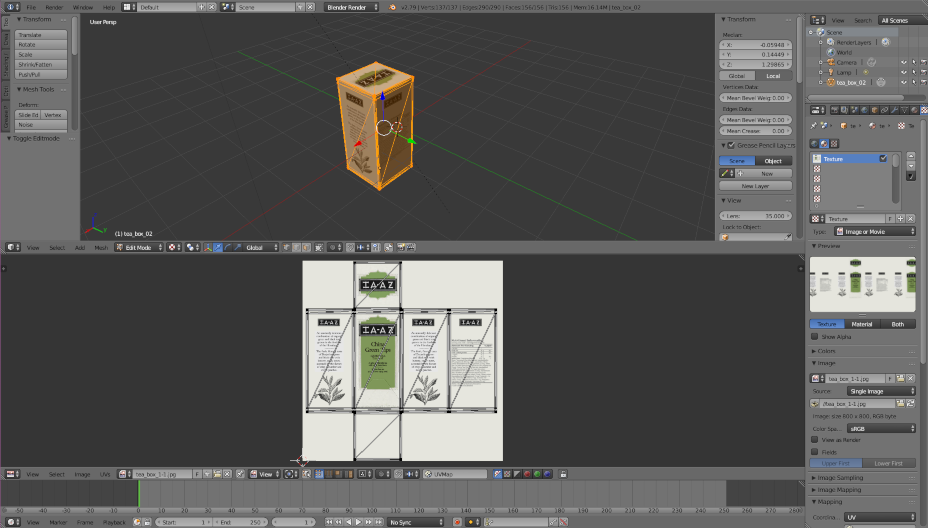
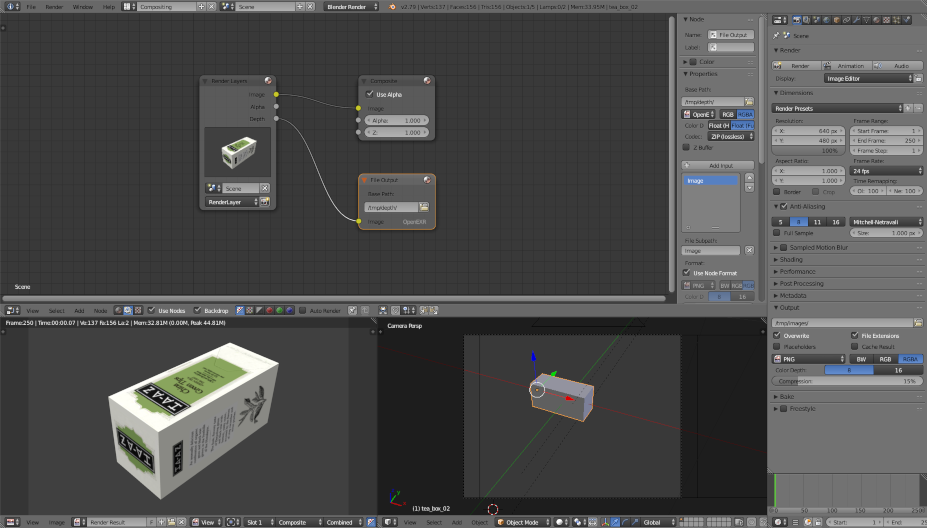
Note The default camera used for rendering should be the one with the black triangle. You can change this with the Scene panel. To create a teabox with texture, we download directly a 3D model here . Then, the rough instructions should be:
select the teabox object
switch to the Texture panel
add a new texture and open the image
switch to the edit mode
switch to the UV/Image Editor and select the image
You should get something similar to this:
See here for more information about texture and UV unwrapping.
This can be done easily:
move the stereo cameras at a desired location / orientation
hit I then LocRotScale to insert a keyframe at the current frame
repeat to perform the desired camera or object movement
Do not forget to add some lights to make the object visible.
Images are generated automatically when rendering the animation (menu Render > Render Animation) and are saved on Ubuntu by default in the /tmp folder. To generate the depth maps, switch to the Compositing screen layout, next to the menu bar:
tick Use Nodes and Backdrop
add a file output node
add a link between the Depth output of the Render Layers node to the File Output node
select the OpenEXR file format
The easiest thing is to run the animation first with the camera used to generate color images and a second time with the one for the depth maps. To switch the main camera, go to the Scene panel and select the desired camera.
The camera poses can be retrieved using the following Python script:
import bpy
import os
from mathutils import *
prefix_pose = "/tmp/camera_poses/"
prefix_image = "/tmp/images/"
def get_camera_pose(cameraName, objectName, scene, frameNumber):
if not os.path.exists(prefix_pose):
os.makedirs(prefix_pose)
M = Matrix().to_4x4()
M[1][1] = -1
M[2][2] = -1
cam = bpy.data.objects[cameraName]
object_pose = bpy.data.objects[objectName].matrix_world
object_pose_normalized = object_pose.copy()
object_orientation_normalized = object_pose_normalized.to_3x3().normalized()
for i in range(3):
for j in range(3):
object_pose_normalized[i][j] = object_orientation_normalized[i][j]
camera_pose = M*cam.matrix_world.inverted()*object_pose_normalized
print("camera_pose:\n" , camera_pose)
filename = prefix_pose + cameraName + "_%03d" % frameNumber + ".txt"
with open(filename, 'w' ) as f:
f.write(str(camera_pose[0][0]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[0][1]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[0][2]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[0][3]) + " " )
f.write("\n" )
f.write(str(camera_pose[1][0]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[1][1]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[1][2]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[1][3]) + " " )
f.write("\n" )
f.write(str(camera_pose[2][0]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[2][1]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[2][2]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[2][3]) + " " )
f.write("\n" )
f.write(str(camera_pose[3][0]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[3][1]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[3][2]) + " " )
f.write(str(camera_pose[3][3]) + " " )
f.write("\n" )
return
def my_handler(scene):
frameNumber = scene.frame_current
print("\n\nFrame Change" , scene.frame_current)
get_camera_pose("Camera" , "tea_box_02" , scene, frameNumber)
step_count = 250
scene = bpy.context.scene
for step in range(1, step_count):
scene.frame_set(step)
if not os.path.exists(prefix_image):
os.makedirs(prefix_image)
scene.render.filepath = (prefix_image + '%04d.png' ) % step
bpy.ops.render.render( write_still=True )
my_handler(scene)
This script will also automatically generate and save the animation images and write the corresponding camera poses.
Note Data are saved in the /tmp/ directory by default and the path should be changed accordingly depending on the OS. Camera and object names should also be changed accordingly. Since depth data are stored in OpenEXR file format, OpenCV is used for the reading. The following C++ sample file also available in tutorial-mb-generic-tracker-rgbd-blender.cpp reads color and depth images, pointcloud is recreated using the depth camera intrinsic parameters and the ground truth data are read and printed along with the estimated camera pose from the model-based tracker.
#include <iostream>
#include <visp3/core/vpDisplay.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpIoTools.h>
#include <visp3/io/vpImageIo.h>
#include <visp3/gui/vpDisplayX.h>
#include <visp3/gui/vpDisplayGDI.h>
#include <visp3/gui/vpDisplayOpenCV.h>
#include <visp3/mbt/vpMbGenericTracker.h>
#if (VISP_HAVE_OPENCV_VERSION >= 0x020403) && defined(VISP_HAVE_PUGIXML)
namespace {
vpImage<uint16_t> &I_depth_raw,
unsigned int &depth_width,
unsigned int &depth_height,
{
char buffer[FILENAME_MAX];
std::stringstream ss;
ss << input_directory << "/images/%04d.jpg" ;
sprintf(buffer, ss.str().c_str(), cpt);
std::string filename_img = buffer;
std::cerr << "Cannot read: " << filename_img << std::endl;
return false ;
}
ss.str("" );
ss << input_directory << "/depth/Image%04d.exr" ;
sprintf(buffer, ss.str().c_str(), cpt);
std::string filename_depth = buffer;
cv::Mat depth_raw = cv::imread(filename_depth, cv::IMREAD_ANYDEPTH | cv::IMREAD_ANYCOLOR);
if (depth_raw.empty()) {
std::cerr << "Cannot read: " << filename_depth << std::endl;
return false ;
}
depth_width = static_cast< unsigned int > (depth_raw.cols);
depth_height = static_cast< unsigned int > (depth_raw.rows);
I_depth_raw.
resize (depth_height, depth_width);
pointcloud.resize(depth_width*depth_height);
for (int i = 0; i < depth_raw.rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < depth_raw.cols; j++) {
I_depth_raw[i][j] = static_cast< uint16_t> (32767.5f * depth_raw.at<cv::Vec3f>(i, j)[0]);
double x = 0.0, y = 0.0;
double Z = depth_raw.at<cv::Vec3f>(i, j)[0] > 2.0f ? 0.0 : static_cast<double>(depth_raw.at<cv::Vec3f>(i, j)[0]);
size_t idx = static_cast< size_t > (i*depth_raw.cols + j);
pointcloud[idx].resize(3);
pointcloud[idx][0] = x*Z;
pointcloud[idx][1] = y*Z;
pointcloud[idx][2] = Z;
}
}
ss.str("" );
ss << input_directory << "/camera_poses/Camera_%03d.txt" ;
sprintf(buffer, ss.str().c_str(), cpt);
std::string filename_pose = buffer;
std::ifstream f_pose;
f_pose.open(filename_pose.c_str());
if (!f_pose.is_open()) {
std::cerr << "Cannot read: " << filename_pose << std::endl;
return false ;
}
cMo_ground_truth.
load (f_pose);
return true ;
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
std::string input_directory = "." ;
std::string config_color = "teabox.xml" , config_depth = "teabox_depth.xml" ;
std::string model_color = "teabox.cao" , model_depth = "teabox.cao" ;
std::string init_file = "teabox.init" ;
std::string extrinsic_file = "depth_M_color.txt" ;
unsigned int first_frame_index = 1;
bool disable_depth = false ;
bool display_ground_truth = false ;
bool click = false ;
for (int i = 1; i < argc; i++) {
if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--input_directory" && i + 1 < argc) {
input_directory = std::string(argv[i + 1]);
} else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--config_color" && i + 1 < argc) {
config_color = std::string(argv[i + 1]);
} else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--config_depth" && i + 1 < argc) {
config_depth = std::string(argv[i + 1]);
} else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--model_color" && i + 1 < argc) {
model_color = std::string(argv[i + 1]);
} else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--model_depth" && i + 1 < argc) {
model_depth = std::string(argv[i + 1]);
} else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--init_file" && i + 1 < argc) {
init_file = std::string(argv[i + 1]);
} else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--extrinsics" && i + 1 < argc) {
extrinsic_file = std::string(argv[i + 1]);
} else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--disable_depth" ) {
disable_depth = true ;
} else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--display_ground_truth" ) {
display_ground_truth = true ;
} else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--click" ) {
click = true ;
} else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--first_frame_index" && i+1 < argc) {
first_frame_index = static_cast< unsigned int > (atoi(argv[i+1]));
}
else if (std::string(argv[i]) == "--help" || std::string(argv[i]) == "-h" ) {
std::cout << "Usage: \n" << argv[0] << " [--input_directory <data directory> (default: .)]"
" [--config_color <object.xml> (default: teabox.xml)] [--config_depth <object.xml> (default: teabox_depth.xml)]"
" [--model_color <object.cao> (default: teabox.cao)] [--model_depth <object.cao> (default: teabox.cao)]"
" [--init_file <object.init> (default: teabox.init)]"
" [--extrinsics <depth to color transformation> (default: depth_M_color.txt)] [--disable_depth]"
" [--display_ground_truth] [--click] [--first_frame_index <index> (default: 1)]" << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
}
std::cout << "input_directory: " << input_directory << std::endl;
std::cout << "config_color: " << config_color << std::endl;
std::cout << "config_depth: " << config_depth << std::endl;
std::cout << "model_color: " << model_color << std::endl;
std::cout << "model_depth: " << model_depth << std::endl;
std::cout << "init_file: " << model_depth << std::endl;
std::cout << "extrinsic_file: " << extrinsic_file << std::endl;
std::cout << "first_frame_index: " << first_frame_index << std::endl;
std::cout << "disable_depth: " << disable_depth << std::endl;
std::cout << "display_ground_truth: " << display_ground_truth << std::endl;
std::cout << "click: " << click << std::endl;
std::vector<int> tracker_types;
if (!disable_depth)
if (!disable_depth)
else
if (!disable_depth)
else
std::cout << "cam_color:\n" << cam_color << std::endl;
std::cout << "cam_depth:\n" << cam_depth << std::endl;
unsigned int depth_width = 0, depth_height = 0;
std::vector<vpColVector> pointcloud;
unsigned int frame_cpt = first_frame_index;
read_data(frame_cpt, input_directory, I, I_depth_raw, depth_width, depth_height, pointcloud, cam_depth, cMo_ground_truth);
#if defined(VISP_HAVE_X11)
#elif defined(VISP_HAVE_GDI)
#else
#endif
d1.
init (I, 0, 0,
"Color image" );
d2.
init (I_depth, static_cast<int>(I.
getWidth ()), 0,
"Depth image" );
if (!disable_depth) {
std::ifstream f_extrinsics;
f_extrinsics.open(extrinsic_file.c_str());
depthMcolor.
load (f_extrinsics);
tracker.setCameraTransformationMatrix("Camera2" , depthMcolor);
std::cout << "depthMcolor:\n" << depthMcolor << std::endl;
}
if (display_ground_truth) {
} else
try {
bool quit = false ;
while (!quit && read_data(frame_cpt, input_directory, I, I_depth_raw, depth_width, depth_height, pointcloud, cam_depth, cMo_ground_truth)) {
if (display_ground_truth) {
} else {
if (!disable_depth) {
std::map<std::string, const vpImage<unsigned char> *> mapOfImages;
std::map<std::string, const std::vector<vpColVector> *> mapOfPointClouds;
std::map<std::string, unsigned int> mapOfPointCloudWidths;
std::map<std::string, unsigned int> mapOfPointCloudHeights;
mapOfImages["Camera1" ] = &I;
mapOfPointClouds["Camera2" ] = &pointcloud;
mapOfPointCloudWidths["Camera2" ] = depth_width;
mapOfPointCloudHeights["Camera2" ] = depth_height;
tracker.
track (mapOfImages, mapOfPointClouds, mapOfPointCloudWidths, mapOfPointCloudHeights);
} else
}
std::cout << "\nFrame: " << frame_cpt << std::endl;
if (!display_ground_truth)
std::cout << "cMo:\n" << cMo << std::endl;
std::cout << "cMo ground truth:\n" << cMo_ground_truth << std::endl;
if (!disable_depth) {
}
else
std::ostringstream oss;
oss << "Frame: " << frame_cpt;
if (!display_ground_truth) {
oss.str("" );
}
switch (button) {
quit = !click;
break ;
click = !click;
break ;
default :
break ;
}
}
frame_cpt++;
}
} catch (std::exception& e) {
std::cerr << "Catch exception: " << e.what() << std::endl;
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
#else
int main()
{
std::cout << "To run this tutorial, ViSP should be built with OpenCV and pugixml libraries." << std::endl;
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
#endif
Note Here the depth values are manually clipped in order to simulate the depth range of a depth sensor. This probably can be done directly in Blender. Once build, to get tutorial-mb-generic-tracker-rgbd-blender.cpp usage, just run:
$ ./tutorial-mb-generic -tracker-rgbd-blender -h
./tutorial-mb-generic -tracker-rgbd-blender [--input_directory <data directory> (default : .)] [--config_color <object .xml> (default : teabox.xml)] [--config_depth <object.xml> (default : teabox_depth.xml)] [--model_color <object .cao> (default : teabox.cao)] [--model_depth <object.cao> (default : teabox.cao)] [--init_file <object .init> (default : teabox.init)] [--extrinsics <depth to color transformation> (default : depth_M_color.txt)] [--disable_depth] [--display_ground_truth] [--click] [--first_frame_index <index> (default : 1)]
Default parameters allow to run the binary with the data provided in ViSP. Just run:
$ ./tutorial-mb-generic -tracker-rgbd-blender
The next video shows the results that you should obtain:
VIDEO
You are now ready to see the next Tutorial: Template tracking .


![\[ \begin{bmatrix} p_x & 0 & u_0 \\ 0 & p_y & v_0 \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \]](form_1332.png)
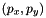
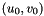
![\[ p_x = \frac{f_{x\text{ in mm}} \times \text{image width in px}}{\text{sensor width in mm}} \]](form_1335.png)