#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpHomogeneousMatrix.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpIoTools.h>
#include <visp3/core/vpMath.h>
#include <visp3/io/vpParseArgv.h>
#include <visp3/robot/vpSimulatorCamera.h>
#include <visp3/visual_features/vpFeatureThetaU.h>
#include <visp3/visual_features/vpFeatureTranslation.h>
#include <visp3/vs/vpServo.h>
#define GETOPTARGS "h"
void usage(const char *name, const char *badparam);
bool getOptions(int argc, const char **argv);
void usage(const char *name, const char *badparam)
{
fprintf(stdout, "\n\
Simulation of a 3D visual servoing:\n\
- eye-in-hand control law,\n\
- velocity computed in the camera frame,\n\
- without display.\n\
\n\
SYNOPSIS\n\
%s [-h]\n", name);
fprintf(stdout, "\n\
OPTIONS: Default\n\
\n\
-h\n\
Print the help.\n");
if (badparam)
fprintf(stdout, "\nERROR: Bad parameter [%s]\n", badparam);
}
bool getOptions(int argc, const char **argv)
{
const char *optarg_;
int c;
switch (c) {
case 'h':
usage(argv[0], NULL);
return false;
break;
default:
usage(argv[0], optarg_);
return false;
break;
}
}
if ((c == 1) || (c == -1)) {
usage(argv[0], NULL);
std::cerr << "ERROR: " << std::endl;
std::cerr << " Bad argument " << optarg_ << std::endl << std::endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main(int argc, const char **argv)
{
try {
if (getOptions(argc, argv) == false) {
exit(-1);
}
std::string username;
std::string logdirname;
#if defined(_WIN32)
logdirname = "C:/temp/" + username;
#else
logdirname = "/tmp/" + username;
#endif
try {
} catch (...) {
std::cerr << std::endl << "ERROR:" << std::endl;
std::cerr << " Cannot create " << logdirname << std::endl;
exit(-1);
}
}
std::string logfilename;
logfilename = logdirname + "/log.dat";
std::ofstream flog(logfilename.c_str());
std::cout << std::endl;
std::cout << "-------------------------------------------------------" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Test program for vpServo " << std::endl;
std::cout << " Eye-in-hand task control, velocity computed in the camera frame" << std::endl;
std::cout << " Simulation " << std::endl;
std::cout << " task : 3D visual servoing " << std::endl;
std::cout << "-------------------------------------------------------" << std::endl;
std::cout << std::endl;
0.1, 0.2, 2,
wMo = wMc * cMo;
0, 0, 1,
t.buildFrom(cMcd);
tu.buildFrom(cMcd);
task.addFeature(t, td);
task.addFeature(tu, tud);
task.setLambda(1);
task.print();
unsigned int iter = 0;
while (iter++ < 200) {
std::cout << "------------------------------------" << iter << std::endl;
tu.buildFrom(cMcd);
v = task.computeControlLaw();
if (iter == 1)
std::cout << "|| s - s* || = " << (task.getError()).sumSquare() << std::endl;
flog << v.
t() <<
" " << (task.getError()).t() << std::endl;
}
task.kill();
flog.close();
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
std::cout << "Catch a ViSP exception: " << e << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
}


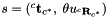 and the desired one
and the desired one 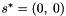 .
.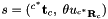 .
.